Meer informatie over het kopen van bitcoins
Met Coinbase wordt het gemakkelijk om uw lokale valuta om te wisselen naar bitcoins en vice versa. Op deze pagina vindt u meer informatie over het kopen van bitcoins en het veilig opslaan ervan in een portemonnee.
Registreren voor Coinbase
De eerste stap is het registreren voor een Coinbase-account. Daarmee hebt u een veilige plaats voor het opslaan van uw bitcoins, en veilige betalingswijzen om uw lokale valuta om te wisselen naar bitcoins en vice versa.


Uw bankrekening koppelen
Nadat u zich hebt geregistreerd, moet u uw bankrekening koppelen. U moet enkele verificatiestappen uitvoeren voordat u het account kunt gebruiken. Zodra de verificatiestappen voltooid zijn, kunt u een aankoop doen.

Bitcoins kopen en verkopen
Nadat u uw eerste aankoop bent gestart, voeren wij uw aankoop uit en leveren wij uw bitcoins af. (Verkopen werkt op dezelfde manier maar dan andersom). De prijs van bitcoins verandert in de loop der tijd, dus we laten u de actuele wisselkoers zien voordat u uw aankoop doet.
Het gemakkelijkste opstapje naar de wereld van de bitcoins
Registreer u vandaag nog voor meer informatie over het kopen van bitcoins.
Bitcoin kopen.com
Bitcoins kopen met IDEAL & koers info
Bitcoin kopen is in een informatieve site die uitleg geeft over bitcoin en het protocol. Daarnaast kunt u hier bitcoins kopen met ideal. Ook delen wij sinds kort ethereum en ether kopen informatie en geven wij informatie over guldens. Bitcoin in het kort: Bitcoin is technisch gezien vergelijkbaar met Napster (De eerste p2p bestanden uitwissel dienst) maar dan op het gebied van geld. Bitcoin kan direct tussen 2 verschillende computers worden uitgewisseld, is bijna niet traceerbaar en zorgt voor veel betaalgemak doordat er geen tussenpartijen zijn, bijna geen wachttijden en bijna geen transactiekosten. Het is geen tastbaar geld maar het zijn in feite cryptografische sleutels die een bepaalde waarde vertegenwoordigen. Deze waarde wordt bepaald door de markt en fluctueert sterk met een steigende tendens.
Meer over Bitcoin:
Om mee te doen heb je de "Bitcoin client" nodig, dit is een stukje software dat functioneert als je "portemonnee", hierna wallet genoemd. In je wallet kan je transacties doen of overmakingen ontvangen van hele bitcoins of fracties van bitcoins. Je kan de bitcoin wallet hier downloaden. Nadat je hem hebt gedownload kon je voorheen wat gratis bitcoin centen krijgen via deze site om te zien hoe het werkt, echter die gratis bitcoins zijn momenteel op. Indien je "Generate coins" activeert gaat het programma Coins voor je genereren. Op een normale computer gaat dat echter veel te langzaam. Een betere optie is deelnemen in een pool om te zoeken naar bitcoins. Verderop vermelden we een aantal "mining pools".
Dit is een screenshot van de bitcoin wallet:
Op het technische vlak schijnt bitcoin goed in elkaar te zitten, de cryptografische sleutels die worden gebruikt kunnen niet worden gekraakt, zelfs niet door supercomputers. Het programma bestaat volledig in het netwerk, elke client (of wallet) heeft een record van de volledige historie van alle transacties in zich waardoor er nooit data verloren kan gaan.
Enkele voordelen van bitcoin:
- Eindgebruiker-Eindgebruiker (p2p)
Het kan direct naar de ontvanger worden gestuurd zonder tussenkomst van banken of andere bureau's
Indien je geld overmaakt van de eigen bitcoin account naar een andere betaal je geen transactiekosten.
Met een click op de muisknop staat het geld op de tegenpartij zijn account, het is net zo snel als een chatbericht sturen, of een e-mail.
Het is een open source project, dit wil zeggen dat de broncode door iedereen bekeken kan worden waardoor er kan worden verwacht dat het geen frauduleus systeem is (anders zou dat snel boven water komen).
Het is net zo gemakkelijk om geld naar bijv. Nieuw Zeeland te sturen als het sturen van een chat berichtje.
Gebruik ervan is vrijwel volledig anoniem, het is vergelijkbaar met cash geld uitgeven, deze uitgaven zijn niet traceerbaar.
Je bent eigen baas over je geld, je besluit zelf naar wie je het overmaakt, banken, overheden of tussenpartijen hebben geen invloed op je uitgaven.
Doordat er nooit meer dan 21 miljoen bitcoins zullen worden uitgegeven lijkt het erop dat deze currency niet gevoelig is voor inflatie.
Enkele nadelen van bitcoin:
- Onderhevig aan deflatie
Doordat er maximaal slechts 21.000.000 bitcoins worden uitgegeven is deze digitale muntsoort wellicht aan speculatie onderhevig waardoor er een constante stijging in waarde kan worden verwacht. Dit is een bedreiging voor het uiteindelijke succes van bitcoin.
Banken en overheden hebben geen vat op bitcoin waardoor zij wellicht naar mogelijkheden gaan zoeken om het te verbieden, zoals de muziekindustrie dat deed met Napster.
Indien het gehacked wordt of anderzins faalt heeft dat grote gevolgen voor de waarde van de bitcoin.
Wellicht is bitcoin niet de uiteindelijk variant van cryptografisch geld die zal overleven maar zullen er nieuwe betere soorten worden ontwikkeld, resulterend in een (totale) devaluatie van bitcoin.
Waar kan ik bitcoin kopen
Hieronder volgt een lijst met bronnen waar bitcoins kunnen worden aangeschaft:
Wat is bitcoin mining
Met bitcoin mining wordt bedoeld het met processorkracht finaliseren van zogenaamde "blocks", blocks zijn in feite verzamelingen transacties die moeten worden gebundeld. Het bitcoin netwerk beloont de computer die de daadwerkelijke afronding van een block berekent met een aantal bitcoins, deze beloning aan bitcoins is overigens geen constante maar is voorgeprogrammeerd om steeds minder te worden na verloop van tijd.
Gebruik deze mining calculator om te berekenen hoeveel je kan verdienen bij de huidige koers.
Waar kan ik meedoen in bitcoin mining pools
Bitcoin mining is dus het proces waarin processorkracht wordt gebruikt om zogenaamde "blocks", verzamelingen van bitcoin transacties, te finaliseren. Hieraan is een beloning gekoppeld van een aantal bitcoins (bijvoorbeeld 25). Indien je aan "solo mining" doet is die beloning van bitcoins geheel voor jezelf, indien je in een mining pool deelneemt wordt de beloning gedeeld door het aantal deelnemers en/of jouw percentage van bijdrage aan processor of videokaart capaciteit. Indien je een gemiddelde computer hebt is het aan te raden niet solo "te minen" maar mee te doen in een pool.
Hieronder volgt een lijstje met bronnen waar bitcoins samen kunnen worden "gemined":
Bitcoin Mining Pools
 Now that you have Bitcoin mining hardware, your next step is to join a Bitcoin mining pool.
Now that you have Bitcoin mining hardware, your next step is to join a Bitcoin mining pool.
What is a Mining Pool?
Mining pools are groups of cooperating miners who agree to share block rewards in proportion to their contributed mining hash power.
While mining pools are desirable to the average miner as they smooth out rewards and make them more predictable, they unfortunately concentrate power to the mining pool’s owner.
Miners can, however, choose to redirect their hashing power to a different mining pool at anytime.
Pool Concentration in China
Before we get into the best mining pools to join, it’s important to note that most mining pools are in China. Many only have Chinese websites and support. Mining centralization in China is one of Bitcoin’s biggest issues at the moment.
There are about 20 major mining pools. Broken down by the percent of hash power controlled by a pool, and the location of that pool’s company, we estimate that Chinese pools control
81% of the network hash rate:
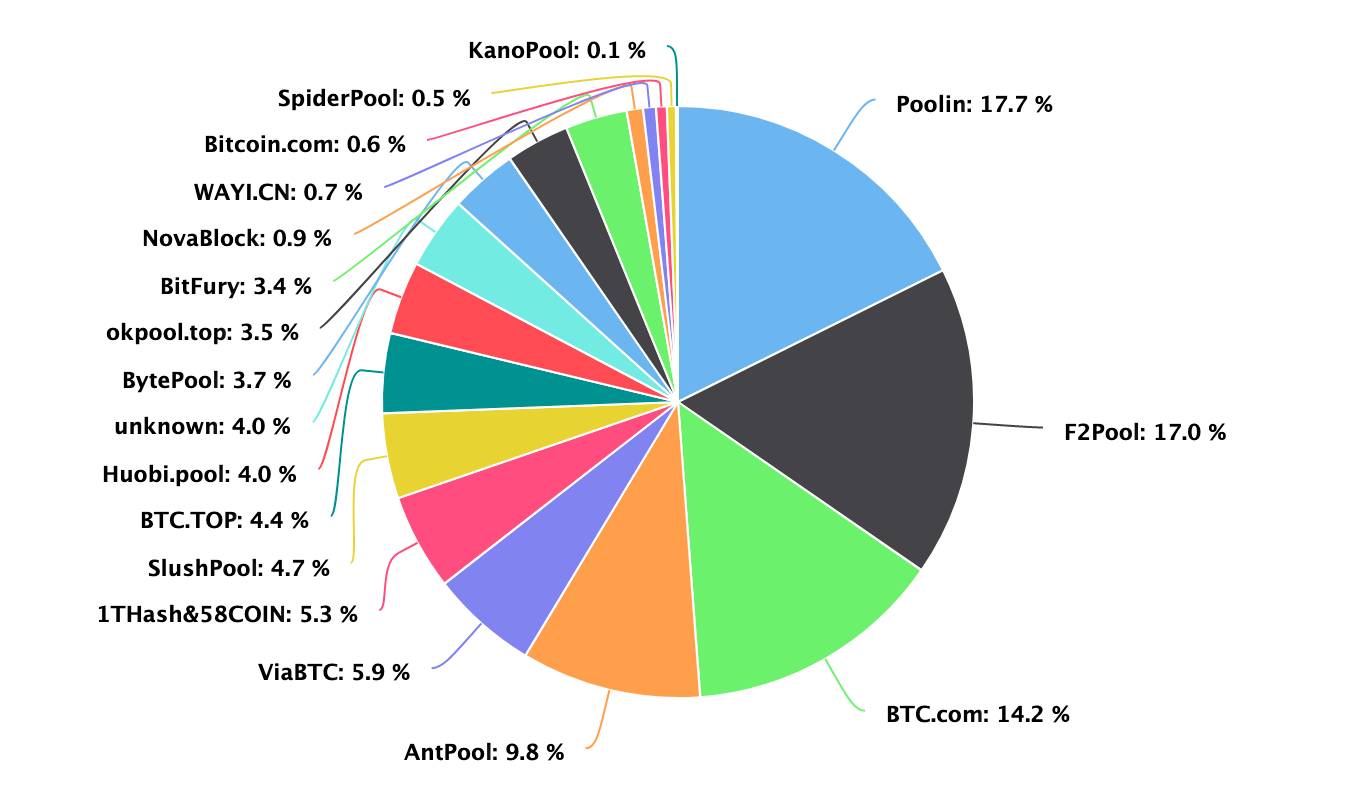
The Biggest Mining Pools
The list below details the biggest Bitcoin mining pools. This is based on info from Blockchain’s pool share chart:
We strongly recommend new miners to join Slush Pool despite it not being one of the biggest pools. It was the first Bitcoin mining pool and remains one of the most reliable and trusted pools, especially for beginners.
BTC.com is a public mining pool that can be joined. However, we strongly recommend joining Slush Pool instead.
Antpool is a mining pool based in China and owned by BitMain. Antpool mines about 25% of all blocks.
ViaBTC is a somewhat new mining pool that has been around for about one year. It’s targeted towards Chinese miners.
Slush was the first mining pool and currently mines about 3% of all blocks.
Slush is probably one of the best and most popular mining pools despite not being one of the largest.
DiscusFish, also known as F2Pool, is based in China. F2Pool has mined about 5-6% of all blocks over the past six months.
BTC.top is a private pool and cannot be joined.
7. Bitclub.Network
Bitclub Network is a large mining pool but appears to be somewhat shady. We recommend staying away from this pool.
BTCC is a pool and also China’s third largest Bitcoin exchange. Its mining pool currently mines about 7% of all blocks.
Bitfury is a private pool that cannot be joined. Bitfury currently mines about 2% of all blocks.
10. BW Pool
BW, established in 2014, is another mining company based in China. It currently mines about 2% of all blocks.
Bitcoin Mining Pool Comparison
The comparison chart above is just a quick reference. The location of a pool does not matter all that much. Most of the pools have servers in every country so even if the mining pool is based in China, you could connect to a server in the US, for example.
Get a Bitcoin Wallet and Mining Software
Before you join a mining pool you will also need Bitcoin mining software and a Bitcoin wallet.
Mining Pools vs Cloud Mining
Many people read about mining pools and think it is just a group that pays out free bitcoins. This is not true! Mining pools are for people who have mining hardware to split profits.
Many people get mining pools confused with cloud mining. Cloud mining is where you pay a service provider to miner for you and you get the rewards.
Just Want Bitcoins?
If you just want bitcoins, mining is NOT the best way to obtain coins.
Buying bitcoins is the EASIEST and FASTEST way to purchase bitcoins.
Get $10 worth of free bitcoins when you buy $100 or more at Coinbase.
Which Countries Mine the most Bitcoins?
Bitcoin mining tends to gravitate towards countries with cheap electricity.
As Bitcoin mining is somewhat centralized, 10-15 mining companies have claimed the vast majority of network hash power.
With many of these companies in the same country, only a number of countries mine and export a significant amount of bitcoins.
China mines the most bitcoins and therefore ends up “exporting” the most bitcoins.
Electricity in China is very cheap and has allowed Chinese Bitcoin miners to gain a very large percentage of Bitcoin’s hash power.
It’s rumored that some Chinese power companies point their excess energy towards Bitcoin mining facilities so that no energy goes to waste.
China is home to many of the top Bitcoin mining companies:
It’s estimated that these mining pools own somewhere around 60% of Bitcoins hash power, meaning they mine about 60% of all new bitcoins.
Georgia is home to BitFury, one of the largest producers of Bitcoin mining hardware and chips. BitFury currently mines about 15% of all bitcoins.
Sweden is home to KnCMiner, a Bitcoin mining company based in Stockholm. KnCMiner currently mines about 7.5% of all bitcoins.
The US is home to 21 Inc., a Bitcoin mining company based in California.
21 runs a large amount of miners, but also sells low powered bitcoin miners as part of their 21 Bitcoin computer.
Most of the hash power from the 21 Bitcoin computers is pointed towards 21’s mining pool. 21 Inc. mines about 3% of all bitcoins.
Other Countries
The countries above mine about 80% of all bitcoins.
The rest of the hash power is spread across the rest of the world, often pointed at smaller mining pools like Slush (Czech Republic) and Eligius (US).
A Note on Pools
While we can see which mining pools are the largest, it’s important to understand that the hash power pointed towards a mining pool isn’t necessarily owned by the mining pool itself.
There are a few cases, like with BitFury and KnCMiner, where the company itself runs the mining operation but doesn’t run a mining pool.
Bitcoin miners can switch mining pools easily by routing their hash power to a different pool, so the market share of pools is constantly changing.
To make the list of top 10 miners, we looked at blocks found over the past 6 months using data from BlockTrail.
The size of mining pools is constantly changing. We will do our best to keep this posted up-to-date.
If you cloud mine then you don’t need to select a pool; the cloud mining company does this automatically.
Why are Miners Important?
Bitcoin miners are crucial to Bitcoin and its security. Without miners, Bitcoin would be vulnerable and easy to attack.
Most Bitcoin users don’t mine.
However, miners are responsible for the creation of all new bitcoins and a fascinating part of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Mining, once done on the average home computer, is now mostly done in large, specialized warehouses with massive amounts of mining hardware.
These warehouses usually direct their hashing power towards mining pools.
Antpool Review
Despite recent controversy, Antpool remains the largest Bitcoin mining pool in terms of its Bitcoin network hash rate. Antpool holds roughly 15% of the total hash rate of all Bitcoin mining pools.

About Antpool
Antpool mined its first block in March 2014, meaning that it emerged roughly four years after the first mining pool; Slushpool.
Antpool is run by Bitmain Technologies Ltd., the world’s largest Bitcoin mining hardware manufacturer, and a large portion of their pool is run on Bitmain’s own mining rigs.
Antpool supports p2pool and stratum mining modes with nodes that are spread all over the world to ensure stability (US, Germany, China etc.).
Also, Antpool’s user interface is surprisingly slick considering that the underlying company thrives mostly off of hardware sales.
How to Join Antpool
The pool is free to join and the process is simple.
First, you need to acquire Bitcoin mining hardware. Then you need to download mining software. If you need help deciding, I suggest you take a look at our hardware and software guides.
Hardware is important because it determines the size of your contribution to the pool’s hash rate. Software is important because it enables you to direct your hardware’s hash power towards the pool you prefer. So make sure to make the right choice in order to optimize your rewards.
Finally, sign up at antpool.com to get started.
What are Antpool’s Fees?
Antpool claims that it does not charge any fees for using its pool. Although there is some truth to this claim, it is not 100% correct.
While Antpool does not directly charge fees, it also does not disclose the Bitcoin transaction fees that are collected. Basically, clients are left in the dark. Currently, every Bitcoin block has a 12.5 BTC reward which Antpool does share with you when it finds a block.
Lately, however, Bitcoin transaction fees have been rising and an additional 1-2 bitcoins are collected per block by pools. At this time, Antpool keeps 1-2 bitcoins form transaction fees for itself, which are not shared with miners who have hash power pointed toward the pool.
It can be argued that these rates prevent the service from being usable for small-time and big-volume users. Consequently, some users on bitcointalk.org heed that the undisclosed fees make the service unwise to use for the time being.
What is the Payout Threshold?
The pool does not appear to have a payout threshold and pays out every day around 10 AM UTC.
The minimum withdrawal amount is 0.0005 BTC (other sources say 0.001 BTC).
Can you do Solo Mining on Antpool?
Solo mining means you mine for bitcoins without joining a pool. So if you use Antpool you are not solo mining by default.
Generally, you will receive more frequent payouts by joining a pool.
What is the Controversy around Antpool?
Antpool has refused to enable arguably beneficial upgrades to Bitcoin for reasons based on claims that have been largely disproved. Notably, this has taken place with somewhat of a vindictive attitude.
More specifically, the controversy revolves around Segwit – a feature that requires miner activation to be enabled. Despite the fact that most Bitcoin users want this feature activated, Antpool, among other pools, appears to be blocking this feature.
Antpool began signaling for Bitcoin Unlimited in early March 2017 for reasons that have not been elucidated by Bitmain CEO (and cofounder Jihan Wu).
Antpool claims that it will only signal for Segwit if there is a hardfork, which is a proposition that most users oppose. Furthermore, allegations that the owner refuses to sell hardware to Segwit supporters have also begun to circulate.
By using Antpool, you allow the pool to decide your hardware’s approach to these matters, meaning that the pool that you used dictates the type of Bitcoin protocol that your hardware employs. If you wish to decide which implementation your hardware should signal for, you can use a pool that leaves the choice to its users, like the Slush mining pool.
Bitfury Information
According to BlockTrail, Bitfury is the third largest Bitcoin mining pool and mines about 11% of all blocks.
The main difference between the Bitfury pool and other mining pools is that Bitfury is a private pool.
Bitfury, the company, makes its own mining hardware and runs its own pool. So, unlike Slush or Antpool, Bitfury cannot be joined if you run mining hardware at home.
Bitfury 16nm ASIC Chip
Unrelated to its pool, Bitfury sells a 16nm ASIC mining chip.
Although Bitfury controls a large portion of the Bitcoin network hash rate, its committed to making Bitcoin decentralized :
BitFury is fundamentally committed to being a responsible player in the Bitcoin community and we want to work with all integrated partners and resellers to make our unique technology widely available ensuring that the network remains decentralized and we move into the exahash era together.
Valery Vavilov, CEO of BitFury
BTCC Mining Pool Review
BTCC Mining Pool is run by BTCC, a Bitcoin company based in China. The company also runs a Bitcoin exchange, wallet, prints physical bitcoins and more!

Worldwide Servers
BTCC runs servers all over the world so your mining hardware can connect easily to the BTCC pool.
So even though BTCC is based in China, don’t be worried that you can’t use or join the pool:
Our mining pool currently has customers from the United States, South America, Europe, China, and Africa.
Bobby Lee, BTCC CEO
Shared Transaction Fees
One great thing about BTCC pool is that it shares Bitcoin transaction fees with its miners.
In every Bitcoin block, around 1-2 BTC worth of transaction fees are also rewarded to the pool.
Some pools keep these fees for themselves and DO NOT share with their miners! BTCC evenly splits the transaction fees among its miners, just like it splits the 12.5 BTC reward.
Slush Pool Review
Slush Pool is run by Satoshi Labs and was the world’s first ever Bitcoin mining pool. It’s advanced yet also a great pool for beginners.
How to Join and Use Slush Pool
Slush Pool is easy to join.
- First, register an account.
- Configure your mining software to point your hardware’s hash power to Slush Pool.
- Enter your Bitcoin wallet address that will receive the payouts.
Here is a helpful video that shows you how to get started:
Slush Mining Pool URLs
According to Slush’s website, there are the current URLs for the mining pool. You will want to point your software towards the URL location closest to you. This will maximize your mining profits.
USA, east coast:
Europe
China, mainland
Asia-Pacific/Singapore:
What are Slush Pool’s Fees?
Slush Pool charges 2% of all payouts.
This may seem like a lot but unlike other pools it shares the transaction fees with its miners. At current levels, these amount to 1-2 BTC more per block.
Satoshi Labs
Satoshi Labs runs Slush Pool. They also make the Bitcoin TREZOR hardware wallet and Coinmap.org.
Ethereum Mining Pool
Many people want to use the pools above for Ethereum too. But, most of the pools listed above are only for Bitcoin mining. Please see our post on Ethereum mining pools for more info on ETH specific pools.
Litecoin Mining Pool
Like Ethereum, none of the pools above support litecoin. For LTC mining you will need separate hardware and a separate pool.
Bitcoin Mining Pool Taxes
You’ll have to consult an accountant or lawyer in your area. But most likely you will have to pay income tax on income from mining pools just like you would for any other type of income.
Transaction fees
Transaction fees are a fee that spenders may include in any Bitcoin transaction. The fee may be collected by the miner who includes the transaction in a block.
Every Bitcoin transaction spends zero or more bitcoins to zero or more recipients. The difference between the amount being spent and the amount being received is the transaction fee (which must be zero or more).
Bitcoin's design makes it easy and efficient for the spender to specify how much fee to pay, whereas it would be harder and less efficient for the recipient to specify the fee, so by custom the spender is almost always solely responsible for paying all necessary Bitcoin transaction fees.
When a miner creates a block proposal, the miner is entitled to specify where all the fees paid by the transactions in that block proposal should be sent. If the proposal results in a valid block that becomes a part of the best block chain, the fee income will be sent to the specified recipient. If a valid block does not collect all available fees, the amount not collected are permanently destroyed; this has happened on more than 1,000 occasions from 2011 to 2017, [1] [2] with decreasing frequency over time.
The market for block space
The minimum fee necessary for a transaction to confirm varies over time and arises from the intersection of supply and demand in Bitcoin's free market for block space. [3] On the supply size, Bitcoin has a maximum block size (currently one million vbytes) that limits the maximum amount of transaction data that can be added to a block.
However, Bitcoin blocks are not produced on a fixed schedule—the system targets an average of one block every 10 minutes over long periods of time but, over short periods of time, a new block can arrive in less than a second or more than an hour after the previous block. As the number of blocks received in a period of time varies, so does the effective maximum block size. For example, in the illustration below we see the average time between blocks based on the time they were received by a node during a one day period (left axis) and the corresponding effective maximum block size implied by that block production rate (right axis, in million vbytes):
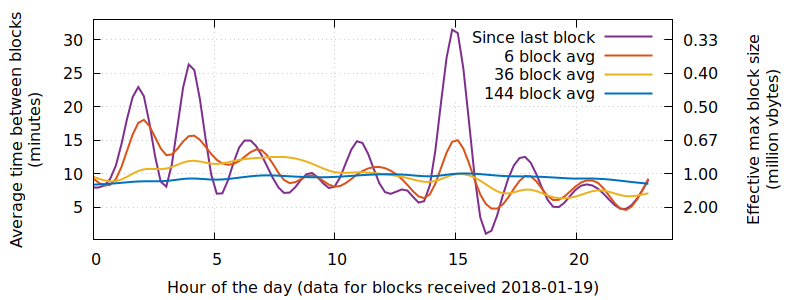
During periods of higher effective maximum block sizes, this natural and unpredictable variability means that transactions with lower fees have a higher than normal chance of getting confirmed—and during periods of lower effective maximum block sizes, low-fee transactions have a lower than normal chance of getting confirmed.
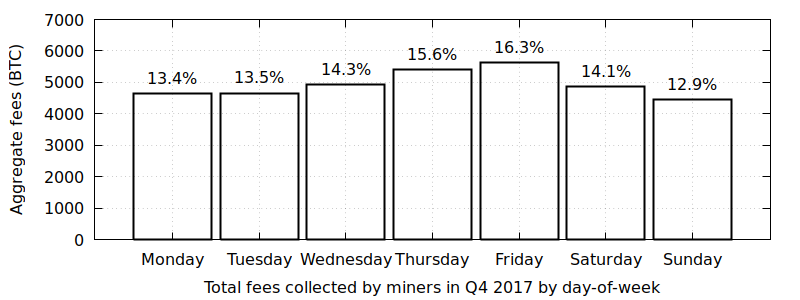
On the demand side of Bitcoin's free market for block space, each spender is under unique constraints when it comes to spending their bitcoins. Some are willing to pay high fees; some are not. Some desire fast confirmation; some are content with waiting a while. Some use wallets with excellent dynamic fee estimation; some do not. In addition, demand varies according to certain patterns, with perhaps the most recognizable being the weekly cycle where fees increase during weekdays and decrease on the weekend:
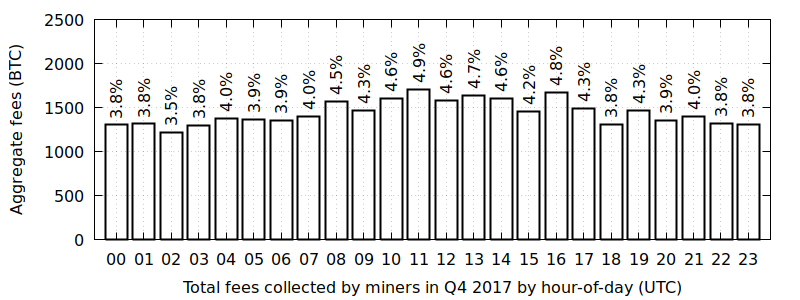
Another less recognizable cycle is the intra-day cycle where fees wax and wane during the day:
These variations in supply and demand create a market for block space that allows users to make a trade-off between confirmation time and cost. Users with high time requirements may pay a higher than average transaction fee to be confirmed quickly, while users under less time pressure can save money by being prepared to wait longer for either a natural (but unpredictable) increase in supply or a (somewhat predictable) decrease in demand.
It is envisioned that over time the cumulative effect of collecting transaction fees will allow those creating new blocks to "earn" more bitcoins than will be mined from new bitcoins created by the new block itself. This is also an incentive to keep trying to create new blocks as the creation of new bitcoins from the mining activity goes towards zero in the future. [4]
Perhaps the most important factor affecting how fast a transaction gets confirmed is its fee rate (often spelled feerate). This section describes why feerates are important and how to calculate a transaction's feerate.
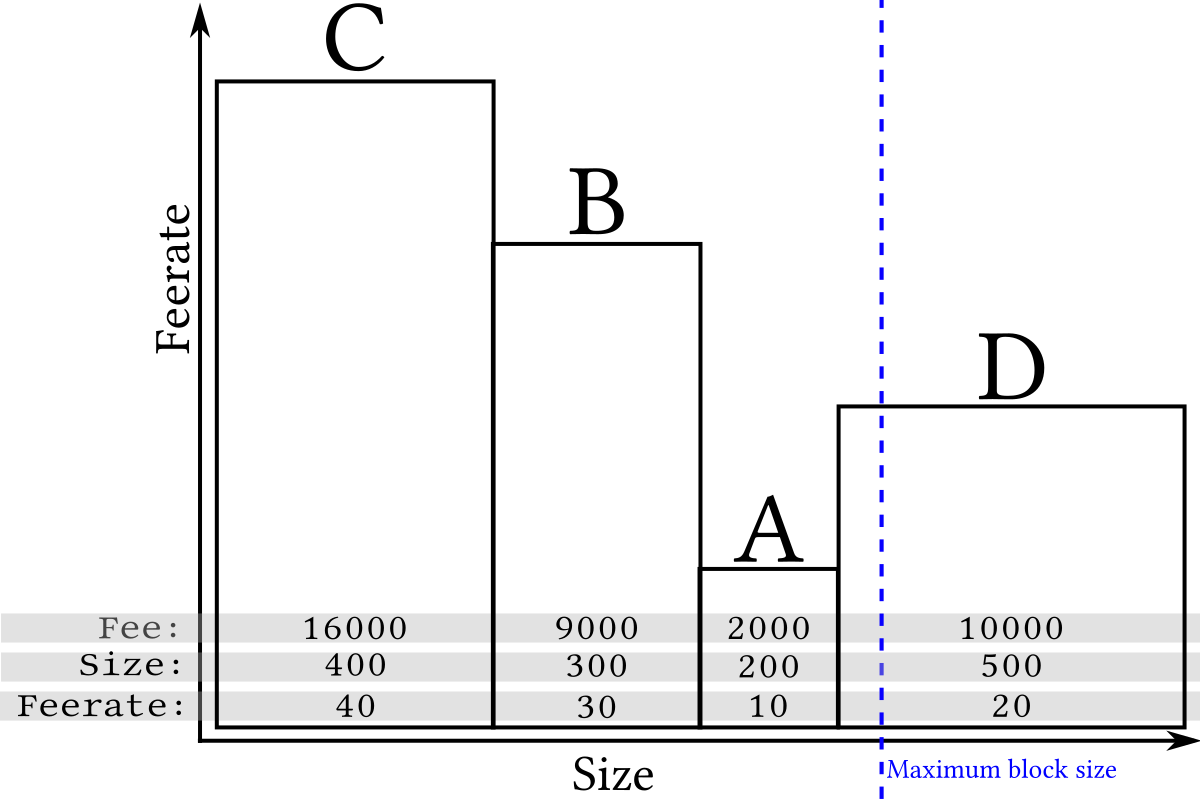
Bitcoin transaction vary in size for a variety of reasons. We can easily visualize that by drawing four transactions side-by-side based on their size (length) with each of our examples larger than the previous one:
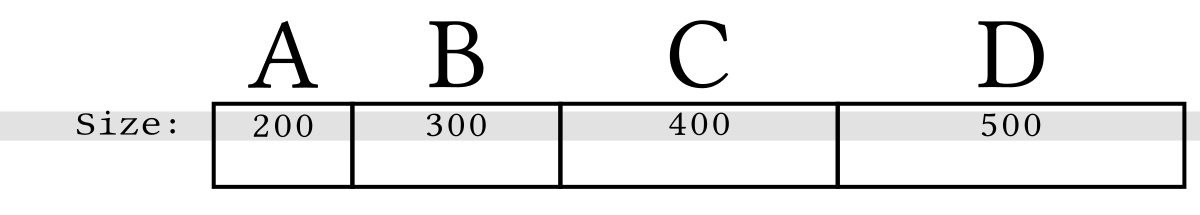
This method of illustrating length maxes it easy to also visualize an example maximum block size limit that constrains how much transaction data a miner can add to an individual block:
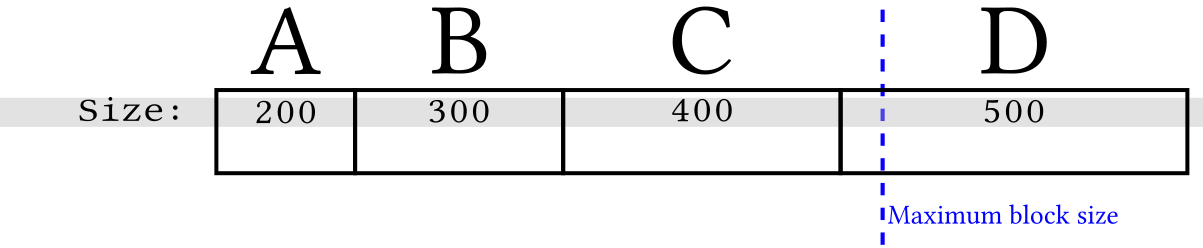
Since Bitcoin only allows whole transactions to be added to a particular block, at least one of the transactions in the example above can't be added to the next block. So how does a miner select which transactions to include? There's no required selection method (called policy) and no known way to make any particular policy required, but one strategy popular among miners is for each individual miner to attempt to maximize the amount of fee income they can collect from the transactions they include in their blocks.
We can add a visualization of available fees to our previous illustration by keeping the length of each transaction the same but making the area of the transaction equal to its fee. This makes the height of each transaction equal to the fee divided by the size, which is called the feerate:
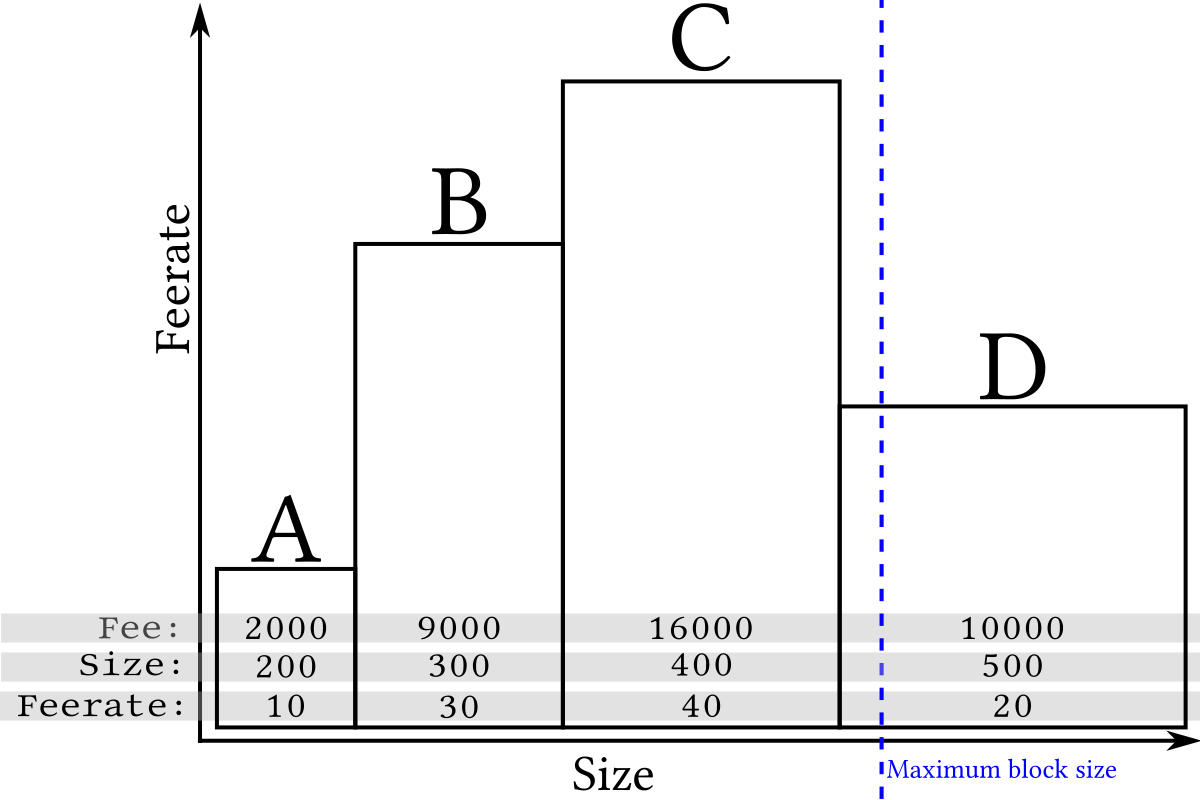
Although long (wide) transactions may contain more total fee, the high-feerate (tall) transactions are the most profitable to mine because their area is greatest compared to the amount of space (length) they take up in a block. For example, compare transaction B to transaction D in the illustration above. This means that miners attempting to maximize fee income can get good results by simply sorting by feerate and including as many transactions as possible in a block:
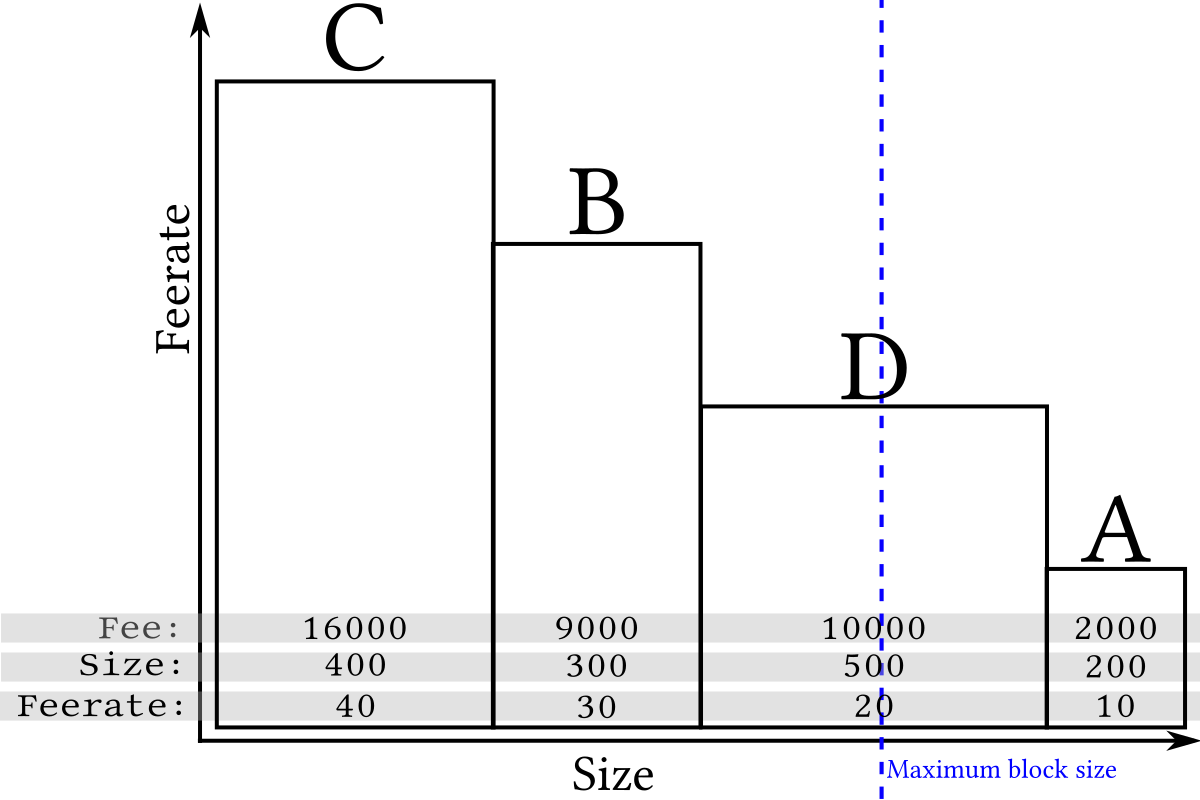
Because only complete transactions can be added to a block, sometimes (as in the example above) the inability to include the incomplete transaction near the end of the block frees up space for one or more smaller and lower-feerate transactions, so when a block gets near full, a profit-maximizing miner will often ignore all remaining transactions that are too large to fit and include the smaller transactions that do fit (still in highest-feerate order):
Excluding some rare and rarely-significant edge cases, the feerate sorting described above maximizes miner revenue for any given block size as long as none of the transactions depend on any of the other transactions being included in the same block (see the next section, feerates for dependent transactions, for more information about that).
To calculate the feerate for your transaction, take the fee the transaction pays and divide that by the size of the transaction (currently based on weight units or vbytes but no longer based on bytes). For example, if a transaction pays a fee of 2,250 nanobitcoins and is 225 vbytes in size, its feerate is 2,250 divided by 225, which is 10 nanobitcoins per vbyte (this happens to be the minimum fee Bitcoin Core Wallet will pay by default).
When comparing to the feerate between several transactions, ensure that the units used for all of the measurements are the same. For example, some tools calculate size in weight units and others use vbytes; some tools also display fees in a variety of denominations.
Feerates for dependent transactions (child-pays-for-parent)
Bitcoin transactions can depend on the inclusion of other transactions in the same block, which complicates the feerate-based transaction selection described above. This section describes the rules of that dependency system, how miners can maximize revenue while managing those dependencies, and how bitcoin spenders can use the dependency system to effectively increase the feerate of unconfirmed transactions.
Each transaction in a block has a sequential order, one transaction after another. Each block in the block chain also has a sequential order, one block after another. This means that there's a single sequential order to every transaction in the best block chain.
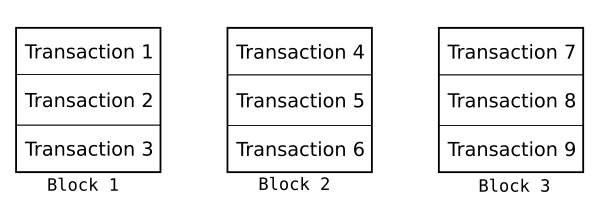
One of Bitcoin's consensus rules is that the transaction where you receive bitcoins must appear earlier in this sequence than the transaction where you spend those bitcoins. For example, if Alice pays Bob in transaction A and Bob uses those same bitcoins to pay Charlie in transaction B, transaction A must appear earlier in the sequence of transactions than transaction B. Often this is easy to accomplish because transaction A appears in an earlier block than transaction B:
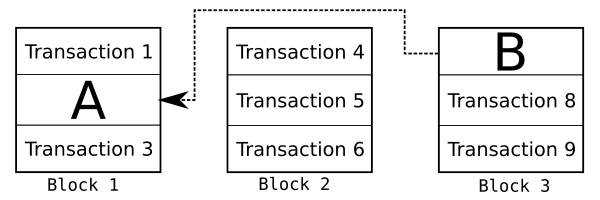
But if transaction A and B both appear in the same block, the rule still applies: transaction A must appear earlier in the block than transaction B.
This complicates the task of maximizing fee revenue for miners. Normally, miners would prefer to simply sort transactions by feerate as described in the feerate section above. But if both transaction A and B are unconfirmed, the miner cannot include B earlier in the block than A even if B pays a higher feerate. This can make sorting by feerate alone less profitable than expected, so a more complex algorithm is needed. Happily, it's only slightly more complex.
For example, consider the following four transactions that are similar to those analyzed in the preceding feerate section:
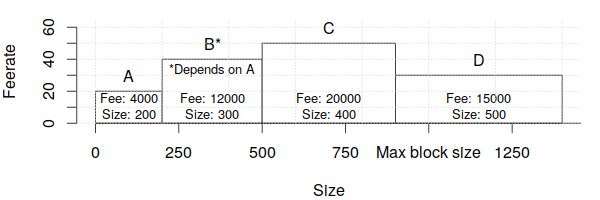
To maximize revenue, miners need a way to compare groups of related transactions to each other as well as to individual transactions that have no unconfirmed dependencies. To do that, every transaction available for inclusion in the next block has its feerate calculated for it and all of its unconfirmed ancestors. In the example, this means that transaction B is now considered as a combination of transaction B plus transaction A:
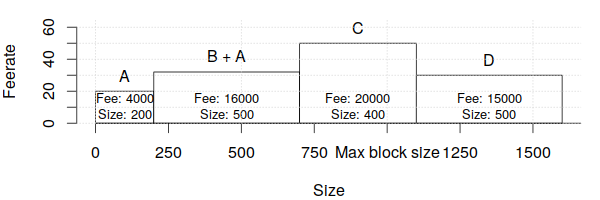
Note that this means that unconfirmed ancestor transactions will be considered twice or more, as in the case of transaction A in our example which is considered once as part of the transaction B+A group and once on its own. We'll deal with this complication in a moment.
These transaction groups are then sorted in feerate order as described in the previous feerate section:
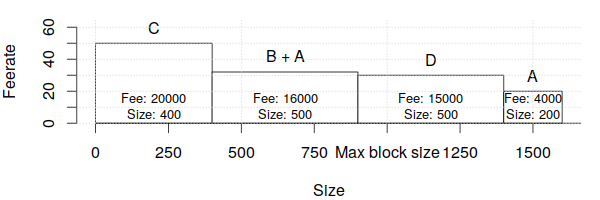
Any individual transaction that appears twice or more in the sorted list has its redundant copies removed. In the example case, we remove the standalone version of transaction A since it's already part of the transaction B+A group:
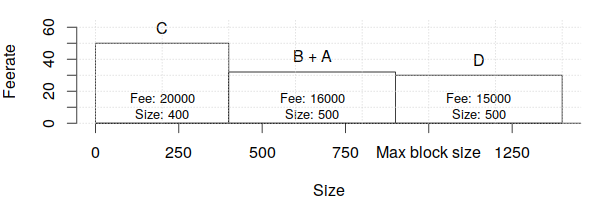
Finally, we see if we can squeeze in some smaller transactions into the end of the block to avoid wasting space as described in the previous feerate section. In this case, we can't, so no changes are made.
Except for some edge cases that are rare and rarely have a significant impact on revenue, this simple and efficient transaction sorting algorithm maximizes miner feerate revenue after factoring in transaction dependencies.
Note: to ensure the algorithm runs quickly, implementations such as Bitcoin Core limit the maximum number of related transactions that will be collected together for consideration as one group. As of Bitcoin Core 0.15.0 (released late 2017), this is a maximum of 25 transactions, although there have been proposals to increase this amount somewhat.
For spenders, miner use of transaction grouping means that if you're waiting for an unconfirmed transaction that pays too low a feerate (e.g. transaction A), you can create a child transaction spending an output of that transaction and which pays a much higher feerate (e.g. transaction B) to encourage miners to confirm both transactions in the same block. Wallets that explicitly support this feature often call it child pays for parent (CPFP) because the child transaction B helps pay for the parent transaction A.
To calculate the feerate for a transaction group, sum the fees paid by all the the group's unconfirmed transactions and divide that by the sum of the sizes for all those same transactions (in weight units or vbytes). For example, if transaction A has a fee of 1,000 nanobitcoins and a size of 250 vbytes and transaction B has a fee of 3,000 nanobitcoins and a size of 150 vbytes, the combined feerate is (1,000 + 3,000)/(250 + 150), which is 10 nanobitcoins per vbyte.
The idea behind ancestor feerate grouping goes back to at least 2013 and saw several different proposals to add it to Bitcoin Core, with it finally becoming available for production with the August 2016 release of Bitcoin Core 0.13.0. [5]
Reference Implementation
The following sections describe the behavior of the reference implementation as of version 0.12.0. Earlier versions treated fees differently, as do other popular implementations (including possible later versions).
Users can decide to pay a predefined fee rate by setting `-paytxfee= ` (or `settxfee ` rpc during runtime). A value of `n=0` signals Bitcoin Core to use floating fees. By default, Bitcoin Core will use floating fees.
Based on past transaction data, floating fees approximate the fees required to get into the `m`th block from now. This is configurable with `-txconfirmtarget= ` (default: `2`).
Sometimes, it is not possible to give good estimates, or an estimate at all. Therefore, a fallback value can be set with `-fallbackfee= ` (default: `0.0002` BTC/kB).
At all times, Bitcoin Core will cap fees at `-maxtxfee= ` (default: 0.10) BTC. Furthermore, Bitcoin Core will never create transactions smaller than the current minimum relay fee. Finally, a user can set the minimum fee rate for all transactions with `-mintxfee=`, which defaults to 1000 satoshis per kB.
Note that a typical transaction is 500 bytes.
Including in Blocks
This section describes how the reference implementation selects which transactions to put into new blocks, with default settings. All of the settings may be changed if a miner wants to create larger or smaller blocks containing more or fewer free transactions.
Then transactions that pay a fee of at least 0.00001 BTC/kb are added to the block, highest-fee-per-kilobyte transactions first, until the block is not more than 750,000 bytes big.
The remaining transactions remain in the miner's "memory pool", and may be included in later blocks if their priority or fee is large enough.
For Bitcoin Core 0.12.0 zero bytes [6] in the block are set aside for the highest-priority transactions. Transactions are added highest-priority-first to this section of the block.
The reference implementation's rules for relaying transactions across the peer-to-peer network are very similar to the rules for sending transactions, as a value of 0.00001 BTC is used to determine whether or not a transaction is considered "Free". However, the rule that all outputs must be 0.01 BTC or larger does not apply. To prevent "penny-flooding" denial-of-service attacks on the network, the reference implementation caps the number of free transactions it will relay to other nodes to (by default) 15 thousand bytes per minute.
Dansk Bitcoinforening
Vi giver værdi til Danmark gennem Bitcoin [Alle kan blive medlem]
Hvad er Bitcoins?
Bitcoin er en digital valuta, som både kan bruges til at betale med, samt til opbevarelse af værdi. Bitcoin er decentralt, hvilket betyder at der ikke er nogen central organisation som bestemmer over Bitcoin, og dermed heller ikke kan lukkes ned. Bitcoin bliver handlet på børser, og det er dermed udbud og efterspørgsel som afgør prisen på en Bitcoin.
Den klassiske forklaring på Bitcoins, er at det er en digital valuta som kan bruges til at betale med. Det giver ikke så meget mening for de fleste, fordi hvordan i al verden kan man bare lave en ny valuta, også begynde at bruge den som et betalingsmiddel?
Før man kan forklare hvad Bitcoins er, så er man først og fremmest nødt til at spørge: Hvad er penge? Penge er et socialt fænomen. Det er en ting mennesker har skabt, for at gøre det nemt at handle. I sig selv er penge intet værd: Pengesedler kan hverken spises eller bruges til at lave smykker. Det er i modsætning til f.eks. guld, som faktisk kan bruges til at lave ting (elektronik, smykker osv.). Penge er i dag noget værd, fordi samfundet tillægger det en værd. Penge har en værdi, fordi butikken på den anden side af gaden tilfældigvis synes at penge er et fint betalingsmiddel, og dermed modtager det når deres købes mad. Det handler derfor om en fælles tillid.
Det samme er tilfældet med Bitcoins. Bitcoins er en valuta som der er skabt via Internettet, og den har i dag en værdi, som gør at du kan betale med den. Faktisk er tilliden i dag så stor til Bitcoins, at den samlede markedsværdi af BItcoins er over 6 milliarder kroner.
Men hvis denne valuta er skabt over Internettet, kan man så ikke bare kopiere den? Kan man ikke bare skabe sin egen nye valuta, og dermed være rig? For at svare på det, skal vi kigge på hvordan Bitcoins blev skabt.
Hvordan blev Bitcoins skabt
I 2009 blev der frigivet en artikel om en ny digital valuta ,som hed Bitcoins. Det var en artikel på 12 sider, udgivet af en anonym person som kaldte sig selv Satoshi Nakamoto. Denne artikel beskrev et avanceret system, hvor man via et P2P netværk (et system hvor alle der har dette program både henter og deler indhold samtidig), kunne opretholde en økonomisk valuta.
Ideen i systemet, er at hvert eneste gang man overfører penge, så gemmes det i en ”blockchain”. Dette skal man bare se som en lang kæde. Forestil dig at du overfører 1 Bitcoin til en kammerat, og han overfører den videre til en butik. Her vil kæden så indeholde informationer der kan fortælle at du overførte 1 BItcoin til din kammerat, og han så overførte den til butikken.
Det revolutionerende omkring denne artikel som blev udgivet, var en måde at håndtere denne kæde på. Alle de som betaler med Bitcoins, deltager i denne kæde, og holder netværket aktivt.
Alle dem som deltager aktivt i netværket, har derfor et lille program på deres computer eller mobile enhed, som kender samtlige betalinger der nogensinde er overført med Bitcoins. Ved at alle har denne kæde, kan man se hvor mange Bitcoins de enkelte brugere har.
Dette bringer os tilbage til værdien af Bitcoins. Spørgsmålet er nemlig: Hvor mange Bitcoins er der? Sagen er at hvis man startede ud med der var flere hundrede millioner af Bitcoins, så ville det ikke være noget som helst værd. Derfor blev Bitcoins laver på en smart måde, hvor der både var et maksimalt antal af Bitcoins, samtidig med at de ikke blev frigivet med det samme.
En meget populær video som forklarer om Bitcoins
Det maskimale antal af bitcoins
Da Bitcoins blev skabt, blev der indbygget en mekanisme som gjorde at BItcoins blev skabt løbende. Den øvre grænse for antallet af Bitcoins er 21.000.000, og de bliver skabt løbende indtil år 2150, hvor samtlige Bitcoins er fundet.
Det betyder at der aldrig nogensinde kan blive skabt mere end 21.000.000 Bitcoins. Dvs. at hvis f.eks. hele USA (med 300.000.000 millioner indbyggere) begyndte at bruge BItcoins som deres valuta, så ville det svare til at der i gennemsnit ville være 0,07 Bitcoins til hver indbygger. Dette er vel og mærke når samtlige Bitcoins er fundet.
Sagen er den at der bruges en matematisk funktion til at bestemme hvor nemt det er at finde Bitcoins. De første Bitcoins var rigtig nemme at finde, hvorimod de så er blevet sværere og sværere at finde. I dag er der fundet ca. 11.000.000 Bitcoins, og det bliver sværere og sværere at finde dem.
”Fundet”? Hvordan kan man finde Bitcoins?
Den skarpe læser ville allerede havde undret sig over sammensætningen af ”fundet Bitcoins”. Vil det sige at man kan finde Bitcoins?
Det som der bl.a. er revolutionerende med Bitcoins, er den måde hvorpå den centrale kæde af betalinger fungerer. Den fungerer ved at der er nogle computere, som arbejder med denne kæde, og finder ud af hvilke betalinger der er sande som skal godkendes og afvises i kæden. Hver gang en kæde finder ud af dette, belønnes den med en meget lille mængde Bitcoins.
Disse computere er drevet af mennesker, som man kalder ”minere”. Udover at arbejde med at godkende/afvise betalinger i den store kæde, så arbejder de også på den store kæde, hvor de kan skabe nye Bitcoins.
Disse computere har installeret nogle softwareprogrammer, som kører i baggrunden. De laver en masse matematiske forsøg, og hver gang der så sker noget rigtigt, så falder der en belønning af. Der er derfor mennesker som tjener deres Bitcoins ved at have disse programmer kørende. Alle kan hente disse programmet, og gå i gang med at finde Bitcoins. Det er dog værd at nævne at den strømregning man får ud af at finde Bitcoins, er væsentligt højere end værdien af de Bitcoins du finder.
Men når man så har fundet sine værdifulde Bitcoins, hvor gemmer man dem så henne? Det gør du i en Bitcoin wallet.
Bitcoins wallet (pung)
Pung hedder på engelsk en wallet, og derfor har man lavet et fint udtryk som hedder ”Bitcoin wallet” (Bitcoin pung).
Begrebet wallet er et begreb som bliver mere og mere udbredt. Et godt eksempel kunne være en PayPal konto, hvor man har nogle penge stående. Et andet eksempel kunne være et gavekort fra Inspiration, hvor man har nogle penge tilbage på sit kort. Konceptet er her at man lavet en ”ny valuta”, som har en værdi i den enkelte butik.
På samme måde samles Bitcoins i wallets. Du har en konto, hvor du har dine Bitcoins gemt. Denne wallet kan så være placeret på din egen computer eller hos en virksomhed på Internettet. Ligesom PayPal opbevarer dine penge, så er der virksomheder såsom Coinbase og Blockchain.info, som opbevarer dine Bitcoins.
Det er afsindigt nemt at oprette en ny wallet. Derfor har de fleste Bitcoins ejere også et par stykker, så de kan have Bitcoins stående rundt omkring.
Når du har denne Bitcoin wallet, så er du også i stand til at bruge dine Bitcoins. Du kan modtage Bitcoins, og du kan sende dem.
Hvordan sender jeg så Bitcoins?
Når der sker en overførsel med Bitcoins, så sker det imellem 2 unikke adresser. Disse adresser kan du tænke på som telefonnumre eller email adresser.
En adresse er en lang tekst. Man plejer ikke at skrive den ind selv, fordi de er meget lange og nærmest umulige at huske. Et eksempel på en adresse kunne være:
I stedet så foregår betalinger ved at man kopierer denne adresse, og indsætter den i ens wallet, hvor man så kan betale. En anden måde at betale på, er ved at scanne en QR-kode med din telefon, også kan du betale via telefonen.
At sende Bitcoins er utrolig simpelt. Du logger ind på din wallet, du kopierer den adresse du ønsker at sende til, indtaster hvor mange Bitcoins du vil sende, også trykker du send. Derefter bliver de overført. Det leder os videre til… Kan man sende mindre end 1 Bitcoin?
Opdelingen af Bitcoins og betalingsgebyrer
Der er jo et maksimum på 21 millioner Bitcoins, og det ville hurtigt kunne give problemer hvis man ikke kunne opdele dem. I så fald ville det kun være de rigeste der ville være i stand til at have 1 Bitcoin, når systemet bliver bare lidt større.
Derfor kan man opdele Bitcoins, så du kan sende 0,01 eller endnu mindre såsom 0,00001 Bitcoins. Den mindste værdi i Bitcoin kaldes en Satoshi, og svarer til en hundrede milliontedel af en Bitcoin. Den mindste værdi er derfor 0,000000001 Bitcoin.
Når man sender Bitcoins, så er der også et transaktionsgebyr. Dette gebyr går ikke til nogen bank, ej heller til en bagmand bag systemet der sidder og skummer fløden. Derimod går dette gebyr til den person som verificerer transaktionen i den lange kæde som holder styr på alle betalingerne (ham der kaldes en miner).
Det transaktionsgebyr man i dag betaler, svarer nærmest til ingenting. Det er et gebyr fast på 0.0005 Bitcoins. Omsat til kroner og øre, så bliver det ca. 20-25 øre, hvilket er langt mindre end normale bankoverførsler. Når du f.eks. handler på en webshop, som tager Visa og lignende kreditkort, betales der som regel imellem 1,5-2% af hele beløbet.
Når værdien af Bitcoins stiger, så vil det også sige at gebyret stiger. Men i Bitcoins er der indbygget et system, hvor dette gebyr vil falde med tiden. Det gør at det vil blive ved med at være forholdsvis lavt, og dermed er konkurrencedygtigt i forhold til kreditkort og normale banker.
Det er vigtigt at der er et betalingsgebyr, fordi kæden med betalingerne ville blive uendelig lang. Det skal derfor ses som en positiv ting, at den er til stede.
Men værdien af Bitcoins… Hvad vil det sige?
Investering i Bitcoins
Bitcoin har i sig selv ikke nogen værdi for omverdenen. Selvfølgelig kan man købe ret mange ting med Bitcoins, men der er ingen central administration for Bitcoins, hvor du kan ombytte dine Bitcoins til en valuta du kender.
Det er der selvfølgelig en masse virksomheder der har lavet, og de er rigtig spændende. På disse websites kan du købe og sælge Bitcoins for dollars of euro.
Der findes bl.a. et stort auktionssite som kaldes MtGox, hvor folk sælger og køber. Det fungerer præcis ligesom med aktier, hvor alle kan gå ind og købe og sælge døgnet rundt. Ud fra udbud og efterspørgsel, fastsættes der hele tiden en pris for Bitcoins.
Denne præcis afspejler hvor meget folk er villige til at betale for en enkelt Bitcoin. I skrivende stund er folk villige til at betale 90$ pr. Bitcoin, men imens du læser dette tal er helt sikkert et helt andet tal.
Det gør også at folk kan investere penge i Bitcoins. Hvis nogen tror på at denne valuta kommer til at stige helt enormt, så kan det være en fordel at investere penge. Det gør man ved at købe Bitcoin, som så stiger eller falder i værdi, også sælger man dem på et senere tidspunkt.
Personligt købte jeg en lille smule Bitcoins da de kostede 13$ pr. Bitcoin, som så i dag er noget mere værd. Så er der andre som har købt dem da de var længere nede i værdi. Grunden til at Bitcoin har steget så meget i værdi, er fordi der er nogle specielle kendetegn, der gør dem meget populære.
Kendetegn ved Bitcoins
Der er en række kendetegn, som gør at det er en helt unik måde at overføre penge på. Dem gennemgår vi her, så du kan få en ide om hvorfor de er blevet så populære som de er.
Man kan ikke trække en betaling tilbage. Et stort problem for mange butikker, er at betalinger udført med nogle kreditkort kan blive ført tilbage. Hvis man sælger produkter, som senere viser sig at have været købt med et stjålet kreditkort, så kan man risikere ikke at modtage pengene. Det er både dyrt og meget ødelæggende for en forretning. Det smarte ved Bitcoins er at når pengene først er modtaget, så er de modtaget, og ingen kan trække dem tilbage.
Bitcoins er decentralt og globalt. I dag kan bankerne afgøre hvem de synes skal have en bankkonto. I Danmark ser vi det selvfølgelig som en selvfølge at alle har en bankkonto, men det er ikke tilfældet i f.eks. Asien og Afrika. Her er det kun et fåtal som har en bankkonto. Med Bitcoins er der ingen som kan beslutte hvem der har lov til at bruge dem. Alle der har adgang til en Internetadgang, som f.eks. på en computercafe, kan bruge dem.
Transaktionsomkostningerne er meget små. Hvis man i dag sender penge på tværs af landegrænser med bankoverførsler, så er det meget dyrt. Med Bitcoins kan man overføre penge hvor betalingen kommer med det samme, og næsten uden gebyr.
Hvad mange borgere ikke ved, er også at kreditkort tager 1,5-2% af alle transaktionsomkostninger ved køb. Det gør at når du køber en mælk i Netto, så er den 1,5-2% dyrere end den burde være, fordi Visa også skal have en del af kagen. I Danmark har vi nogle af verdens mindste gebyrer, så i andre lande er det kæmpe stort.
Bitcoins kan ikke spores. I dag er der ”Big Brother samfund” overalt. Alle pengeoverførsler kan spores, og der er ikke noget privatliv tilbage hvis man endelig gerne vil findes. Bitcoins derimod er anonymt. Du kan lave anonyme betalinger, som ikke kan spores tilbage til dig.
Tekniske forklaringer.
Yderligere forklaringer? Der er en række hjemmesider som forklarer om Bitcoins, og her ønsker vi løbende at linke til flere af dem:
Bitcoins Kaufen
Schnell, Sicher und Rentabel
Gibt es eine Möglichkeit Bitcoins ohne eine Gebühr zu kaufen?
Heute ist es einfach BTC mit einer realen Währung zu kaufen. Dies kann auf verschiedene Arten erfolgen – durch den Tausch mit einem Tauschservice, über einen persönlichen Tausch mit jemanden den man kennt… Aber natürlich, wenn Sie einen Kryptowährung wie Bitcoin kaufen, will jeder Geld sparen und Gebühren vermeiden, vor allem wenn der Betrag größer ist lohnt sich dies. Darum die Frage: Ist es möglich, Bitcoins ohne eine Gebühr zu kaufen? Wie und wo kann man das tun?
Lassen Sie uns beginnen mit der Tatsache, dass alle Tauschservices immer einen kleinen Prozentsatz an Gebühren berechnen. Zum Beispiel ist die Rolle eines Tauschservices die eines Vermittlers, zwischen demjenigen der eine Währung kaufen will und demjenigen der sie verkaufen will. Die Besitzer der Seite benutzen dabei einen spezielle Algorithmus und nehmen alle Risiken für die Durchführung der Transaktion auf sich – und natürlich die Sicherheit, dass für den Tausch auch eine Zahlung für die Dienstleistung erfolgt.
Doch manchmal gibt es Websiten, die angeblich ganz ohne Gebühr arbeiten. Dies sind entweder sehr junge Portale, die durch diese Art Kunden gewinnen wollen, oder sie haben andere versteckte Gebühren, die dann beim Kauf von BTC anfallen. So gibt es Beispiel Auktionen für die Sie zwar beim Tausch Gebühren zahlen müssen, diese aber bei der Bezahlung über eine Kreditkarte wieder gutgeschrieben bekommen.
Tauscher arbeiten nach einem anderen Prinzip. Der Service hat seine eigenen Kryptowährungsanteile und verkauft sie im Tausch gegen eine ordentliche Währung. Er berechnet dabei eine Gebühr für den geleisteten Tausch. Auf der Webseite des Tauschservice können diese festgelegt werden, wie genau die Zahlung durchgeführt wird, aber dann in der Regel mit einer Rate, die sich von der offiziellen unterscheidet. Durchsuchen Sie daher immer sorgfältig die Kurse von bestimmten Websiten und vergleichen sie diese mit den offiziellen Daten.
Der deal ohne vermittler
Eigentlich kann man Bitcoins ohne Gebühr nur in einem Fall kaufen – wenn Sie Bitcoins bei einem persönlichen Treffen kaufen. Dies können Sie auf verschiedene Arten tun. Beispielsweise können Sie in Foren und spezialisierten Webseiten nach Tauschpartner suchen, die Bitcoins verkaufen und anschließend einen Kaufpreis festlegen mit dem beide Seite zufrieden sind.
Sie können auch bei sogenannten Satoshi Meetups teilnehmen – die in verschiedenen Städten auf der ganzen Welt stattfinden. Die Teilnehmer treffen sich alle zwei Wochen an einem bestimmten Ort, um unter Gleichgesinnten gemeinsam mehr über die Kryprowährung zu lernen und darüber zu. Jeder kann bei solchen Treffen teilnehmen, den die Gruppen sind immer froh neue Teilnehmer zu begrüßen.
Denken Sie daran, dass Sie bereits ein eröffnetes Bitcoin-Konto haben und die Anwendung auf ihrem Mobiltelefon installiert haben müssen, um Bitcoins zu kaufen. Wenn Sie jemanden finden, der bereit ist BTC zu verkaufen, müssen Sie nur das Echtgeld an das Bankkonto des Verkäufers überweisen, einen QR-Code in Ihrem Konto erzeugen, und der Verkäufer scannt den Code und transferiert die BTC mit dessen Hilfe an Sie.
Seien sie vorsichtig!
Vergessen Sie dabei nicht, dass die Bitcoin-Transaktionen nicht rückgängig gemacht werden können, so dass Sie Kryptowährungen nur von vertrauenswürdigen Personen kaufen und zweifelhafte Angebote ausweichen sollten. Wenn Sie auf einen Tauschservice stoßen, der keine Schutzmaßnahmen in Form von Zertifikaten hat, Referenzen von Kunden, Lizenzen von den Banken und Zahlungssysteme, ist es besser, diesen Tauschservice zu meiden, um Ihre Bitcoins nicht zu gefährden.
In einigen Ländern wurden bereits BTC-Terminals und Geldautomaten eröffnet, in dem Sie auch Bitcoins gegen die jeweilige nationale Währung kaufen können. Solche Geräte sind mit dem Internet verbunden und tauscht das echte Geld elektronisch und in Echtzeit mit einem festen Wechselkurs um. Aber wir sollten uns nicht täuschen lassen, denn das Gerät berechnet Gebühren, da auch der Betreiber etwas verdienen möchte. Daher kann es in vielen Fällen sogar teurer sein, als ein Kauf bei einem Tauschservice im Internet.
Bitcoin Mission Statement. Or What Does It Mean Sharing Economy and Distributed Trust?
15 Pages Posted: 5 Nov 2015
Dmitri Kosten
3D Business Solutions
Date Written: October 31, 2015
Technological advancements in the means of production are the driving force behind the changes in the prevailing system of socio-economic relations. Feudalism was transformed into capitalism as a result of such advancements. While man obtained physical freedom, the financial freedom remained under the control of the centralized authority.
Keywords: Bitcoin, Blockchain, Crypto-Socialism, socio-economic transformation, socio-economic framework, smart contract, sharing economy, distributed trust, function of money, financial decentralization, financial desintermediation
JEL Classification: A11, A12, A13, A14, A22, A23, A29, A20, B14, B15, B19, B22, B24, B29, B30, B40, E10, E11, E19, E12
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Что такое биткоин?
У каждого государства есть своя валюта. В Эстонии - евро, в России - рубли, а у США - доллары. Мы обмениваем деньги в банках или в специальных обменных пунктах, пересылаем их в любую точку мира и инвестируем. В наше время инновационных технологий, логично, что все переводы идут через Интернет.
Стоит ли удивляться, что в Интернете появилась своя собственная криптовалюта, такая как биткойн? Интерес общества к данной системе появился в конце 2013 года после резких скачков курса криптовалюты биткоин, но начнем с начала. Итак, в 2009 году никому неизвестный программист под псевдонимом Сатоши Накамото создал электронные деньги, т.е. криптовалюту. Функции такой валюты те же, что и у обычной: средство обмена, сбережения и расчетная единица. К тому же у валюты есть спрос, а значит, и свой курс. Но есть существенное отличие: мы не можем увидеть, скажем, почувствовать деньги на ощупь, потому что валюта цифровая и ее функционирование происходит децентрализовано в распределенной компьютерной сети.
Как работает биткоин?
Если, обычно, для перевода денег нам нужно использовать посредников, как правило, банк, то с криптовалютой все проще – деньги передаются напрямую продавцу. А это означает, что, благодаря этому свойству, перед нами открываются новые возможности.
Криптовалюта состоит из монет, а именно из математических хэш-кодов. Такой код уникален, но имеет неудобную читабельность с последовательностью из 27-34 латинских букв и цифр.
Важный момент состоит в том, что любая криптовалюта создается посредством процесса «майнинг» (от англ. Data mining - добыча данных, интеллектуальный анализ данных, глубинный анализ данных). Для такого процесса нужен сверхмощный ПК для решения сложных математических задач. Есть также специальные приложения, биржи и пирамиды для генерации монет, но это уже - последствия электронной валюты.
На самом деле, слишком уж сложна эта система. «Майнинг» позволяет постепенно писать код новых биткоинов и приводит к возникновению закодированных единиц оплаты, которые не привязаны к имени человека и могут храниться в закрытых кошельках или на жестком диске. Мы можем видеть только совершенные транзакции и количество биткоинов у пользователя. Отправить электронные деньги можно в любую точку мира, но перевод производится только в шестнадцатеричном формате.
Плюсы и минусы криптовалюты
«Биткоин» – это первая децентрализованная и неподконтрольная валюта, а значит, нет инфляции, потому что количество монет в системе растет с определенной скоростью, в зависимости от спроса и предложения людей, а максимально возможное значение - 21 млн биткоинов. К тому же, она полностью анонимна, как утверждают информационные порталы, и обладает множеством иных превосходных качеств. Например, все данные системы хранятся в открытом коде на носителях пользователей, а за переводы средств не снимается комиссия.
Но по утверждению портала «bitcoin journal», система биткоин не совсем анонимна, конечно, там нет паспортных данных, но вычислить отправителя на основе анализа транзакций можно, поэтому данное достоинство можно прировнять и к недостаткам.
К минусам также можно отнести «оффлайн кошелек». Он устанавливается на ПК и зашифровывается, но при неисправности жесткого диска навсегда теряется доступ и к средствам. Так, например, британец в 2009 году произвел 7,5 тысяч биткоинов на своем компьютере, но из-за случайности, в виде разлитого кофе, разобрал его, а позже выбросил жесткий диск вовсе. В то же время в новостях появились сведения о росте курса криптовалюты, и мужчина, отправившись на свалку, так и не нашел свой жесткий диск, потеряв при этом миллионы долларов. Таких историй довольно много, потому что раньше монеты биткоин можно было «добывать» и на обычном ПК, но эта валюта не была в цене, вернее, люди не воспринимали ее, как евро или доллары.
И все же, что такое биткоин?
Это пиринговая электронная платежная система. Если раньше можно было заработать на биткоин, поддерживая сеть и занимаясь майнингом, то на текущий момент все изменилось не в лучшую сторону. Нужен мощный ПК, который стоит приличных денег и быстро устаревает, а значит, при вложении в это уже теряются деньги. В случае с инвестированием тоже пока непонятно, выгодна ли сделка, потому что, покупая сейчас биткоины за реальные деньги, мы не можем знать, какой курс валюты будет в дальнейшем. Единственный выход, как утверждает официальный сайт «bitcoin», – это имея свой магазин, продавать товары за криптовалюту, но и с этим возникают сложности. Несколько месяцев назад Министерство финансов РФ выдвинуло предложение запретить данный способ оплаты на территории своей страны. А значит, люди пока не до конца разобрались с понятием биткоин и не воспринимают это, как платёжное средство или возможность заработать, скорее, как очередную пирамиду.
Пока неизвестно, станет ли в будущем криптовалюта единственно верной платежной формой или останется в прошлом, но пока есть спрос - будет и предложение.
Bitcoins Kaufen
Schnell, Sicher und Rentabel
Gibt es eine Möglichkeit Bitcoins ohne eine Gebühr zu kaufen?
Heute ist es einfach BTC mit einer realen Währung zu kaufen. Dies kann auf verschiedene Arten erfolgen – durch den Tausch mit einem Tauschservice, über einen persönlichen Tausch mit jemanden den man kennt… Aber natürlich, wenn Sie einen Kryptowährung wie Bitcoin kaufen, will jeder Geld sparen und Gebühren vermeiden, vor allem wenn der Betrag größer ist lohnt sich dies. Darum die Frage: Ist es möglich, Bitcoins ohne eine Gebühr zu kaufen? Wie und wo kann man das tun?
Lassen Sie uns beginnen mit der Tatsache, dass alle Tauschservices immer einen kleinen Prozentsatz an Gebühren berechnen. Zum Beispiel ist die Rolle eines Tauschservices die eines Vermittlers, zwischen demjenigen der eine Währung kaufen will und demjenigen der sie verkaufen will. Die Besitzer der Seite benutzen dabei einen spezielle Algorithmus und nehmen alle Risiken für die Durchführung der Transaktion auf sich – und natürlich die Sicherheit, dass für den Tausch auch eine Zahlung für die Dienstleistung erfolgt.
Doch manchmal gibt es Websiten, die angeblich ganz ohne Gebühr arbeiten. Dies sind entweder sehr junge Portale, die durch diese Art Kunden gewinnen wollen, oder sie haben andere versteckte Gebühren, die dann beim Kauf von BTC anfallen. So gibt es Beispiel Auktionen für die Sie zwar beim Tausch Gebühren zahlen müssen, diese aber bei der Bezahlung über eine Kreditkarte wieder gutgeschrieben bekommen.
Tauscher arbeiten nach einem anderen Prinzip. Der Service hat seine eigenen Kryptowährungsanteile und verkauft sie im Tausch gegen eine ordentliche Währung. Er berechnet dabei eine Gebühr für den geleisteten Tausch. Auf der Webseite des Tauschservice können diese festgelegt werden, wie genau die Zahlung durchgeführt wird, aber dann in der Regel mit einer Rate, die sich von der offiziellen unterscheidet. Durchsuchen Sie daher immer sorgfältig die Kurse von bestimmten Websiten und vergleichen sie diese mit den offiziellen Daten.
Der deal ohne vermittler
Eigentlich kann man Bitcoins ohne Gebühr nur in einem Fall kaufen – wenn Sie Bitcoins bei einem persönlichen Treffen kaufen. Dies können Sie auf verschiedene Arten tun. Beispielsweise können Sie in Foren und spezialisierten Webseiten nach Tauschpartner suchen, die Bitcoins verkaufen und anschließend einen Kaufpreis festlegen mit dem beide Seite zufrieden sind.
Sie können auch bei sogenannten Satoshi Meetups teilnehmen – die in verschiedenen Städten auf der ganzen Welt stattfinden. Die Teilnehmer treffen sich alle zwei Wochen an einem bestimmten Ort, um unter Gleichgesinnten gemeinsam mehr über die Kryprowährung zu lernen und darüber zu. Jeder kann bei solchen Treffen teilnehmen, den die Gruppen sind immer froh neue Teilnehmer zu begrüßen.
Denken Sie daran, dass Sie bereits ein eröffnetes Bitcoin-Konto haben und die Anwendung auf ihrem Mobiltelefon installiert haben müssen, um Bitcoins zu kaufen. Wenn Sie jemanden finden, der bereit ist BTC zu verkaufen, müssen Sie nur das Echtgeld an das Bankkonto des Verkäufers überweisen, einen QR-Code in Ihrem Konto erzeugen, und der Verkäufer scannt den Code und transferiert die BTC mit dessen Hilfe an Sie.
Seien sie vorsichtig!
Vergessen Sie dabei nicht, dass die Bitcoin-Transaktionen nicht rückgängig gemacht werden können, so dass Sie Kryptowährungen nur von vertrauenswürdigen Personen kaufen und zweifelhafte Angebote ausweichen sollten. Wenn Sie auf einen Tauschservice stoßen, der keine Schutzmaßnahmen in Form von Zertifikaten hat, Referenzen von Kunden, Lizenzen von den Banken und Zahlungssysteme, ist es besser, diesen Tauschservice zu meiden, um Ihre Bitcoins nicht zu gefährden.
In einigen Ländern wurden bereits BTC-Terminals und Geldautomaten eröffnet, in dem Sie auch Bitcoins gegen die jeweilige nationale Währung kaufen können. Solche Geräte sind mit dem Internet verbunden und tauscht das echte Geld elektronisch und in Echtzeit mit einem festen Wechselkurs um. Aber wir sollten uns nicht täuschen lassen, denn das Gerät berechnet Gebühren, da auch der Betreiber etwas verdienen möchte. Daher kann es in vielen Fällen sogar teurer sein, als ein Kauf bei einem Tauschservice im Internet.
Bitcoin Mining Calculator
Got your shiny new ASIC miner? Wondering when it will pay off? If you enter your hash rate below, this page will calculate your expected earnings in both Bitcoins and dollars over various time periods (day, week, and month). It will not attempt to extrapolate difficulty or price changes -- it provides only instantaneous calculations (how much you'd make if all conditions remained as they were right now).
Next difficulty retarget occurs at block 526175.0 (eta 8.0 days): 4.42338107336e+12 / +2.7% [est.]
Has this service helped you? BTC 1MW6BNqwU4StysayHwApDZPBggms25tf5t

CoinBought: Buy anything on Amazon for BTC, ETC, XMR, or more. Orders placed automatically in minutes.
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий