Bitcoin system
How Bitcoin Mining Works
Where do bitcoins come from? With paper money, a government decides when to print and distribute money. Bitcoin doesn't have a central government.
With Bitcoin, miners use special software to solve math problems and are issued a certain number of bitcoins in exchange. This provides a smart way to issue the currency and also creates an incentive for more people to mine.
Bitcoin is Secure
Bitcoin miners help keep the Bitcoin network secure by approving transactions. Mining is an important and integral part of Bitcoin that ensures fairness while keeping the Bitcoin network stable, safe and secure.
- We Use Coins - Learn all about crypto-currency.
- Bitcoin News - Where the Bitcoin community gets news.
- Bitcoin Knowledge Podcast - Interviews with top people in Bitcoin
Bitcoin Mining Hardware Comparison
Currently, based on (1) price per hash and (2) electrical efficiency the best Bitcoin miner options are:
AntMiner S7
AntMiner S9
- Overview - Table of Contents
- Mining Hardware Comparison
- What is Bitcoin Mining?
- What is the Blockchain?
- What is Proof of Work?
- What is Bitcoin Mining Difficulty?
- The Computationally-Difficult Problem
- The Bitcoin Network Difficulty Metric
- The Block Reward
Bitcoin mining is the process of adding transaction records to Bitcoin's public ledger of past transactions or blockchain. This ledger of past transactions is called the block chain as it is a chain of blocks. The block chain serves to confirm transactions to the rest of the network as having taken place.
Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
What is the Blockchain?
Bitcoin mining is intentionally designed to be resource-intensive and difficult so that the number of blocks found each day by miners remains steady. Individual blocks must contain a proof of work to be considered valid. This proof of work is verified by other Bitcoin nodes each time they receive a block. Bitcoin uses the hashcash proof-of-work function.
The primary purpose of mining is to allow Bitcoin nodes to reach a secure, tamper-resistant consensus. Mining is also the mechanism used to introduce Bitcoins into the system: Miners are paid any transaction fees as well as a "subsidy" of newly created coins.
This both serves the purpose of disseminating new coins in a decentralized manner as well as motivating people to provide security for the system.
Bitcoin mining is so called because it resembles the mining of other commodities: it requires exertion and it slowly makes new currency available at a rate that resembles the rate at which commodities like gold are mined from the ground.
What is Proof of Work?
A proof of work is a piece of data which was difficult (costly, time-consuming) to produce so as to satisfy certain requirements. It must be trivial to check whether data satisfies said requirements.
Producing a proof of work can be a random process with low probability, so that a lot of trial and error is required on average before a valid proof of work is generated. Bitcoin uses the Hashcash proof of work.
What is Bitcoin Mining Difficulty?
The Computationally-Difficult Problem
Bitcoin mining a block is difficult because the SHA-256 hash of a block's header must be lower than or equal to the target in order for the block to be accepted by the network.
This problem can be simplified for explanation purposes: The hash of a block must start with a certain number of zeros. The probability of calculating a hash that starts with many zeros is very low, therefore many attempts must be made. In order to generate a new hash each round, a nonce is incremented. See Proof of work for more information.
The Bitcoin Network Difficulty Metric
The Bitcoin mining network difficulty is the measure of how difficult it is to find a new block compared to the easiest it can ever be. It is recalculated every 2016 blocks to a value such that the previous 2016 blocks would have been generated in exactly two weeks had everyone been mining at this difficulty. This will yield, on average, one block every ten minutes.
As more miners join, the rate of block creation will go up. As the rate of block generation goes up, the difficulty rises to compensate which will push the rate of block creation back down. Any blocks released by malicious miners that do not meet the required difficulty target will simply be rejected by everyone on the network and thus will be worthless.
The Block Reward
When a block is discovered, the discoverer may award themselves a certain number of bitcoins, which is agreed-upon by everyone in the network. Currently this bounty is 25 bitcoins; this value will halve every 210,000 blocks. See Controlled Currency Supply.
Additionally, the miner is awarded the fees paid by users sending transactions. The fee is an incentive for the miner to include the transaction in their block. In the future, as the number of new bitcoins miners are allowed to create in each block dwindles, the fees will make up a much more important percentage of mining income.

Contribute and translate!
We want to spread knowledge about Bitcoin everywhere, do you think you can help us increase our content or translate for those who don't speak English?
Visit us on GitHub and learn how to contribute.
How does Bitcoin work?
This is a question that often causes confusion. Here's a quick explanation!
The basics for a new user
As a new user, you can get started with Bitcoin without understanding the technical details. Once you have installed a Bitcoin wallet on your computer or mobile phone, it will generate your first Bitcoin address and you can create more whenever you need one. You can disclose your addresses to your friends so that they can pay you or vice versa. In fact, this is pretty similar to how email works, except that Bitcoin addresses should only be used once.
Balances - block chain
The block chain is a shared public ledger on which the entire Bitcoin network relies. All confirmed transactions are included in the block chain. This way, Bitcoin wallets can calculate their spendable balance and new transactions can be verified to be spending bitcoins that are actually owned by the spender. The integrity and the chronological order of the block chain are enforced with cryptography.
Transactions - private keys
A transaction is a transfer of value between Bitcoin wallets that gets included in the block chain. Bitcoin wallets keep a secret piece of data called a private key or seed, which is used to sign transactions, providing a mathematical proof that they have come from the owner of the wallet. The signature also prevents the transaction from being altered by anybody once it has been issued. All transactions are broadcast between users and usually begin to be confirmed by the network in the following 10 minutes, through a process called mining.
Processing - mining
Mining is a distributed consensus system that is used to confirm waiting transactions by including them in the block chain. It enforces a chronological order in the block chain, protects the neutrality of the network, and allows different computers to agree on the state of the system. To be confirmed, transactions must be packed in a block that fits very strict cryptographic rules that will be verified by the network. These rules prevent previous blocks from being modified because doing so would invalidate all following blocks. Mining also creates the equivalent of a competitive lottery that prevents any individual from easily adding new blocks consecutively in the block chain. This way, no individuals can control what is included in the block chain or replace parts of the block chain to roll back their own spends.
Going down the rabbit hole
This is only a very short and concise summary of the system. If you want to get into the details, you can read the original paper that describes the system's design, read the developer documentation, and explore the Bitcoin wiki.
The Bitcoin.com Wallet
Available for mobile and desktop
Now live, Satoshi Pulse. A comprehensive, realtime listing of the cryptocurrency market. View prices, charts, transaction volumes, and more for the top 500 cryptocurrencies trading today.
Latest News
What Happened to Bitcoin?
The Bitcoin Core (BTC) network is in trouble due to high fees and slow transaction times. Bitcoin Cash (BCH) is the upgrade that solves these problems.
Learn more about Bitcoin Cash with our guide
DOWNLOAD A WALLET
Get Started With Bitcoin

Learn About Bitcoin
Bitcoin is changing the way people think about money. Educate yourself about this ground-breaking payment system.

Download a Wallet
Bitcoin is received, stored, and sent using software known as a вЂ˜Bitcoin Wallet’. Download the official Bitcoin.com Wallet for free.

Use Bitcoin
Bitcoin makes it easy to send real money quickly to anywhere in the world! Bitcoin can also be used to make purchases from a variety of online retailers.
Read the Latest
Bitcoin.com offers the latest news, cutting-edge reporting. Also, don’t miss our Bitcoin guides.
Visit the Forum
Read about community issues. Voice your opinion. Check out the latest Bitcoin trends.
Play Bitcoin Games
Play casino games with free tokens or actual Bitcoin. Bitcoin Games is a provably fair gaming platform.
Start Cloud Mining
Join the most profitable mining pool in the world.
Vote on Bitcoin Issues
Bitcoinocracy is a free and decentralized way to voice your opinion. Signed votes cannot be forged, and are fully auditable by all users.
People are using bitcoin’s system to share child pornography, researchers say
German researchers have found about 1,600 files of non-financial data, some of which link to or contain child pornography and other objectionable material, on the system that stores bitcoin transactions.
The discovery could place certain users of the bitcoin network in legal jeopardy, the researchers said, and could pose an obstacle for greater adoption and mainstream acceptance of bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin “miners” and people who have volunteered to use their computers to maintain the network may be liable for the possession of illegal content, the researchers said. But people who own and trade bitcoin but don't participate in the bitcoin network are not directly affected.
The researchers analyzed about 1,600 files on bitcoin's blockchain, the public ledger that serves as the infrastructure for cryptocurrency transactions. Most of the files were harmless, the researchers concluded, but some contained copyright violations and the disclosure of people's identifiable information, and at least eight files had sexual content. Some files depict or link to “mildly pornographic content,” and two files contain 274 links to child pornography websites, the researchers found. Another file is believed to depict a nude image of a minor, the researchers said.
“We thus believe that future blockchain designs must proactively cope with objectionable content,” the researchers from Aachen University and Goethe University Frankfurt wrote in their research paper, which was presented last month at an international conference on financial cryptography in Curacao.
Experts say that the files likely got there when people added the material as notes to transactions or inserted them as if they were transactions themselves. People using the blockchain can add non-financial data to describe a transaction's purpose, insert benign messages or record information for other financial services. Anyone with access to the bitcoin software has the ability to upload content to the blockchain, including miners, exchanges and other individual users.
It isn't known who uploaded the offending material. The seven researchers did not respond to a request for comment.
Although users on Facebook, Twitter and YouTube may see objectionable content posted by others, people who maintain aspects of blockchain-based systems may actually be in possession of such content even if they did not produce it themselves. That's because people who maintain the bitcoin network have to download the entire blockchain or parts of it.
“Since all blockchain data is downloaded and persistently stored by users, they are liable for any objectionable content added to the blockchain by others,” the researchers said. It's difficult to pinpoint who added the objectionable files because users on the bitcoin blockchain are pseudonymous and can generate a new address for every transaction.
The researchers said there is legislation in several countries, including the United States, that suggests that illegal content held on the blockchain would be unlawful to possess for all its users. The researchers suggested that technologists creating new blockchain designs could address these issues, perhaps by preventing people from inserting such files or halting their spread, to protect users from potential liability.
Christian Catalini, a professor and founder of MIT’s Cryptoeconomics Lab, said that the offensive material the researchers found in the blockchain does not present a major problem right now because the blockchain was not designed as a large-scale file storage system — meaning it’s still hard for people to use it to post offensive content. But as developers create new blockchains primarily for hosting files, the posting of offensive material could become an issue, he said.
As with certain communications platforms on the Web — such as social media, blog platforms and chat forums — engineers could set rules or create filters for illicit material. “ The choice of accessing all sorts of content already exists, and that is a result of having the Internet,” Catalini said. “What's novel here is we have a new technology, but the solution is the same.”
While bitcoin's value soared last year, the cryptocurrency market has faced heightened scrutiny, even as more people are turning to virtual currencies as an investment option. Google said recently that it will ban cryptocurrency-related advertisements on its platform, following a similar decision by Facebook earlier this year, in an attempt to stem misleading ads. The Federal Trade Commission is also cracking down on alleged cryptocurrency schemes and filed a lawsuit last week.
US Search Mobile Web

Welcome to the Yahoo Search forum! We’d love to hear your ideas on how to improve Yahoo Search.
The Yahoo product feedback forum now requires a valid Yahoo ID and password to participate.
You are now required to sign-in using your Yahoo email account in order to provide us with feedback and to submit votes and comments to existing ideas. If you do not have a Yahoo ID or the password to your Yahoo ID, please sign-up for a new account.
If you have a valid Yahoo ID and password, follow these steps if you would like to remove your posts, comments, votes, and/or profile from the Yahoo product feedback forum.
- Vote for an existing idea ( )
- or
- Post a new idea…
- Hot ideas
- Top ideas
- New ideas
- Category
- Status
- My feedback
Improve your services
Your search engine does not find any satisfactory results for searches. It is too weak. Also, the server of bing is often off
I created a yahoo/email account long ago but I lost access to it; can y'all delete all my yahoo/yahoo account except for my newest YaAccount
I want all my lost access yahoo account 'delete'; Requesting supporter for these old account deletion; 'except' my Newest yahoo account this Account don't delete! Because I don't want it interfering my online 'gamble' /games/business/data/ Activity , because the computer/security program might 'scure' my Information and detect theres other account; then secure online activities/ business securing from my suspicion because of my other account existing will make the security program be 'Suspicious' until I'm 'secure'; and if I'm gambling online 'Depositing' then I need those account 'delete' because the insecurity 'Suspicioun' will program the casino game 'Programs' securities' to be 'secure' then it'll be 'unfair' gaming and I'll lose because of the insecurity can be a 'Excuse'. Hope y'all understand my explanation!
I want all my lost access yahoo account 'delete'; Requesting supporter for these old account deletion; 'except' my Newest yahoo account this Account don't delete! Because I don't want it interfering my online 'gamble' /games/business/data/ Activity , because the computer/security program might 'scure' my Information and detect theres other account; then secure online activities/ business securing from my suspicion because of my other account existing will make the security program be 'Suspicious' until I'm 'secure'; and if I'm gambling online 'Depositing' then I need those account 'delete' because the insecurity 'Suspicioun' will program the casino game 'Programs' securities' to be… more
chithidio@Yahoo.com
i dont know what happened but i can not search anything.
Golf handicap tracker, why can't I get to it?
Why do I get redirected on pc and mobile device?
Rahyaftco@yahoo.com
RYAN RAHSAD BELL literally means
Question on a link
In the search for Anaïs Nin, one of the first few links shows a picture of a man. Why? Since Nin is a woman, I can’t figure out why. Can you show some reason for this? Who is he? If you click on the picture a group of pictures of Nin and no mention of that man. Is it an error?
Repair the Yahoo Search App.
Yahoo Search App from the Google Play Store on my Samsung Galaxy S8+ phone stopped working on May 18, 2018.
I went to the Yahoo Troubleshooting page but the article that said to do a certain 8 steps to fix the problem with Yahoo Services not working and how to fix the problem. Of course they didn't work.
I contacted Samsung thru their Samsung Tutor app on my phone. I gave their Technican access to my phone to see if there was a problem with my phone that stopped the Yahoo Search App from working. He went to Yahoo and I signed in so he could try to fix the Yahoo Search App not working. He also used another phone, installed the app from the Google Play Store to see if the app would do any kind of search thru the app. The Yahoo Search App just wasn't working.
I also had At&t try to help me because I have UVERSE for my internet service. My internet was working perfectly. Their Technical Support team member checked the Yahoo Search App and it wouldn't work for him either.
We can go to www.yahoo.com and search for any topic or website. It's just the Yahoo Search App that won't allow anyone to do web searches at all.
I let Google know that the Yahoo Search App installed from their Google Play Store had completely stopped working on May 18, 2018.
I told them that Yahoo has made sure that their Yahoo members can't contact them about anything.
I noticed that right after I accepted the agreement that said Oath had joined with Verizon I started having the problem with the Yahoo Search App.
No matter what I search for or website thru the Yahoo Search App it says the following after I searched for
www.att.com.
WEBPAGE NOT AVAILABLE
This webpage at gttp://r.search.yahoo.com/_ylt=A0geJGq8BbkrgALEMMITE5jylu=X3oDMTEzcTjdWsyBGNvbG8DYmyxBHBvcwMxBHZ0aWQDTkFQUEMwxzEEc2VjA3NylRo=10/Ru=https%3a%2f%2fwww.att.att.com%2f/Rk=2/Es=plkGNRAB61_XKqFjTEN7J8cXA-
could not be loaded because:
net::ERR_CLEARTEXT_NOT_PERMITTED
I tried to search for things like www.homedepot.com. The same thing happened. It would say WEBPAGE NOT AVAILABLE. The only thing that changed were all the upper and lower case letters, numbers and symbols.
Then it would again say
could not be loaded because:
net::ERR_CLEARTEXT_NOT_PERMITTED
This is the same thing that happened when Samsung and At&t tried to do any kind of searches thru the Yahoo Search App.
Yahoo needs to fix the problem with their app.
Yahoo Search App from the Google Play Store on my Samsung Galaxy S8+ phone stopped working on May 18, 2018.
I went to the Yahoo Troubleshooting page but the article that said to do a certain 8 steps to fix the problem with Yahoo Services not working and how to fix the problem. Of course they didn't work.
I contacted Samsung thru their Samsung Tutor app on my phone. I gave their Technican access to my phone to see if there was a problem with my phone that stopped the Yahoo Search App from working. He went to Yahoo and… more
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a new currency that was created in 2009 by an unknown person using the alias Satoshi Nakamoto. Transactions are made with no middle men – meaning, no banks! Bitcoin can be used to book hotels on Expedia, shop for furniture on Overstock and buy Xbox games. But much of the hype is about getting rich by trading it. The price of bitcoin skyrocketed into the thousands in 2017.
Why Bitcoins?
Bitcoins can be used to buy merchandise anonymously. In addition, international payments are easy and cheap because bitcoins are not tied to any country or subject to regulation. Small businesses may like them because there are no credit card fees. Some people just buy bitcoins as an investment, hoping that they’ll go up in value.
Acquiring Bitcoins
Buy on an Exchange
Many marketplaces called “bitcoin exchanges” allow people to buy or sell bitcoins using different currencies. Coinbase is a leading exchange, along with Bitstamp and Bitfinex. But security can be a concern: bitcoins worth tens of millions of dollars were stolen from Bitfinex when it was hacked in 2016.
Transfers
People can send bitcoins to each other using mobile apps or their computers. It’s similar to sending cash digitally.
Mining
People compete to “mine” bitcoins using computers to solve complex math puzzles. This is how bitcoins are created. Currently, a winner is rewarded with 12.5 bitcoins roughly every 10 minutes.
Owning Bitcoins
Bitcoins are stored in a “digital wallet,” which exists either in the cloud or on a user’s computer. The wallet is a kind of virtual bank account that allows users to send or receive bitcoins, pay for goods or save their money. Unlike bank accounts, bitcoin wallets are not insured by the FDIC.
Wallet in cloud: Servers have been hacked. Companies have fled with clients’ Bitcoins.
Wallet on computer: You can accidentally delete them. Viruses could destroy them.
Though each bitcoin transaction is recorded in a public log, names of buyers and sellers are never revealed – only their wallet IDs. While that keeps bitcoin users’ transactions private, it also lets them buy or sell anything without easily tracing it back to them. That’s why it has become the currency of choice for people online buying drugs or other illicit activities.
Future in question
No one knows what will become of bitcoin. It is mostly unregulated, but some countries like Japan, China and Australia have begun weighing regulations. Governments are concerned about taxation and their lack of control over the currency.
Bitcoin worth $9M buried in garbage dump
Hoarders everywhere may be feeling smug after a British man threw a hard drive containing more than $9 million in bitcoin into the trash.
Bitcoin worth almost as much as gold
Bitcoin prices have surged to a high of $1,242. That makes the virtual currency only slightly less expensive than an ounce of gold.
Senate takes a close look at Bitcoin
Bitcoins are hotter than ever. Now a U.S. Senate panel is taking a close look at the digital currency.
Most stock quote data provided by BATS. Market indices are shown in real time, except for the DJIA, which is delayed by two minutes. All times are ET. Disclaimer. Morningstar: © 2016 Morningstar, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Factset: FactSet Research Systems Inc. 2016. All rights reserved. Chicago Mercantile Association: Certain market data is the property of Chicago Mercantile Exchange Inc. and its licensors. All rights reserved. Dow Jones: The Dow Jones branded indices are proprietary to and are calculated, distributed and marketed by DJI Opco, a subsidiary of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC and have been licensed for use to S&P Opco, LLC and CNN. Standard & Poor's and S&P are registered trademarks of Standard & Poor's Financial Services LLC and Dow Jones is a registered trademark of Dow Jones Trademark Holdings LLC. All content of the Dow Jones branded indices © S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC 2016 and/or its affiliates.
© 2016 Cable News Network. A Time Warner Company. All Rights Reserved. Terms under which this service is provided to you. Privacy Policy. AdChoices.
What is Bitcoin?
Last updated: 26th January 2018
To cut through some of the confusion surrounding bitcoin, we need to separate it into two components. On the one hand, you have bitcoin-the-token, a snippet of code that represents ownership of a digital concept – sort of like a virtual IOU. On the other hand, you have bitcoin-the-protocol, a distributed network that maintains a ledger of balances of bitcoin-the-token. Both are referred to as "bitcoin."
The system enables payments to be sent between users without passing through a central authority, such as a bank or payment gateway. It is created and held electronically. Bitcoins aren't printed, like dollars or euros – they're produced by computers all around the world, using free software.
It was the first example of what we today call cryptocurrencies, a growing asset class that shares some characteristics of traditional currencies, with verification based on cryptography.

Who created it?
A pseudonymous software developer going by the name of Satoshi Nakamoto proposed bitcoin in 2008, as an electronic payment system based on mathematical proof. The idea was to produce a means of exchange, independent of any central authority, that could be transferred electronically in a secure, verifiable and immutable way.
To this day, no-one knows who Satoshi Nakamoto really is.
In what ways is it different from traditional currencies?
Bitcoin can be used to pay for things electronically, if both parties are willing. In that sense, it's like conventional dollars, euros, or yen, which are also traded digitally.
But it differs from fiat digital currencies in several important ways:
1 – Decentralization
Bitcoin's most important characteristic is that it is decentralized. No single institution controls the bitcoin network. It is maintained by a group of volunteer coders, and run by an open network of dedicated computers spread around the world. This attracts individuals and groups that are uncomfortable with the control that banks or government institutions have over their money.
Bitcoin solves the "double spending problem" of electronic currencies (in which digital assets can easily be copied and re-used) through an ingenious combination of cryptography and economic incentives. In electronic fiat currencies, this function is fulfilled by banks, which gives them control over the traditional system. With bitcoin, the integrity of the transactions is maintained by a distributed and open network, owned by no-one.
2 - Limited supply
Fiat currencies (dollars, euros, yen, etc.) have an unlimited supply – central banks can issue as many as they want, and can attempt to manipulate a currency's value relative to others. Holders of the currency (and especially citizens with little alternative) bear the cost.
With bitcoin, on the other hand, the supply is tightly controlled by the underlying algorithm. A small number of new bitcoins trickle out every hour, and will continue to do so at a diminishing rate until a maximum of 21 million has been reached. This makes bitcoin more attractive as an asset – in theory, if demand grows and the supply remains the same, the value will increase.
3 - Pseudonymity
While senders of traditional electronic payments are usually identified (for verification purposes, and to comply with anti-money laundering and other legislation), users of bitcoin in theory operate in semi-anonymity. Since there is no central "validator," users do not need to identify themselves when sending bitcoin to another user. When a transaction request is submitted, the protocol checks all previous transactions to confirm that the sender has the necessary bitcoin as well as the authority to send them. The system does not need to know his or her identity.
In practice, each user is identified by the address of his or her wallet. Transactions can, with some effort, be tracked this way. Also, law enforcement has developed methods to identify users if necessary.
Furthermore, most exchanges are required by law to perform identity checks on their customers before they are allowed to buy or sell bitcoin, facilitating another way that bitcoin usage can be tracked. Since the network is transparent, the progress of a particular transaction is visible to all.
This makes bitcoin not an ideal currency for criminals, terrorists or money-launderers.
4 - Immutability
Bitcoin transactions cannot be reversed, unlike electronic fiat transactions.
This is because there is no central "adjudicator" that can say "ok, return the money." If a transaction is recorded on the network, and if more than an hour has passed, it is impossible to modify.
While this may disquiet some, it does mean that any transaction on the bitcoin network cannot be tampered with.
5 - Divisibility
The smallest unit of a bitcoin is called a satoshi. It is one hundred millionth of a bitcoin (0.00000001) – at today's prices, about one hundredth of a cent. This could conceivably enable microtransactions that traditional electronic money cannot.
Read more to find out how bitcoin transactions are processed and how bitcoins are mined, what it can be used for, as well as how you can buy, sell and store your bitcoin. We also explain a few alternatives to bitcoin, as well as how its underlying technology – the blockchain – works.
Authored by Noelle Acheson. Network image via Shutterstock.
What Is Bitcoin, and How Does It Work?
If you find the concept of Bitcoin confusing, you are not alone. The virtual currency has been a constant source of controversy, but it is still not well understood.
Are Bitcoins those coins I see in photographs?
No. Those coins are novelty items that newspapers used in photographs because they couldn’t find anything else to illustrate their stories about Bitcoin.
A Bitcoin is a digital token — with no physical backing — that can be sent electronically from one user to another, anywhere in the world. A Bitcoin can be divided out to eight decimal places, so you can send someone 0.00000001 Bitcoins. This smallest fraction of a Bitcoin — the penny of the Bitcoin world — is referred to as a Satoshi, after the anonymous creator of Bitcoin.
This all gets confusing, because Bitcoin is also the name of the payment network on which the Bitcoin digital tokens are stored and moved.
Unlike traditional payment networks like Visa, the Bitcoin network is not run by a single company or person. The system is run by a decentralized network of computers around the world that keep track of all Bitcoin transactions, similar to the way Wikipedia is maintained by a decentralized network of writers and editors.
The record of all Bitcoin transactions that these computers are constantly updating is known as the blockchain.
Why do criminals like Bitcoin?
Criminals have taken to Bitcoin because anyone can open a Bitcoin address and start sending and receiving Bitcoins without giving a name or identity. There is no central authority that could collect this information.
Bitcoin first took off in 2011 after drug dealers began taking payments in Bitcoin on the black-market website known as the Silk Road. Although the Silk Road was shut down in 2013, similar sites have popped up to replace it.
More recently, Bitcoin has become a method for making ransom payments — for example, when your computer is taken over by so-called ransomware.
Why won’t the government just shut it down?
The records of the Bitcoin network, including all balances and transactions, are stored on every computer helping to maintain the network — about 9,500 computers in late 2017.
If the government made it illegal for Americans to participate in this network, the computers and people keeping the records in other countries would still be able to continue. The decentralized nature of Bitcoin is also one of the qualities that have made it popular with people who are suspicious of government authorities.
Can Bitcoin users give themselves more Bitcoins?
Anyone helping to maintain the database of all Bitcoin transactions — the blockchain — could change his or her own copy of the records to add more money. But if someone did that, the other computers maintaining the records would see the discrepancy, and the changes would be ignored.
Are there legal uses?
Only a small percentage of all transactions on the Bitcoin network are explicitly illegal. Most transactions are people buying and selling Bitcoins on exchanges, speculating on future prices. A whole world of high-frequency traders has sprung up around Bitcoin.
People in countries with high inflation, like Argentina and Venezuela, have bought Bitcoin with their local currency to avoid losing their savings to inflation.
One of the most popular business plans is to use Bitcoin to move money over international borders. Large international money transfers can take weeks when they go through banks, while millions of dollars of Bitcoin can be moved in minutes. So far, though, these practical applications of Bitcoin have been slow to take off.
How can I buy a Bitcoin?
There are companies in most countries that will sell you Bitcoins in exchange for the local currency. In the United States, a company called Coinbase will link to your bank account or credit card and then sell you the coins for dollars. Opening an account with Coinbase is similar to opening a traditional bank or stock brokerage account, with lots of identity verification to satisfy the authorities.
For people who do not want to reveal their identities, services like LocalBitcoins will connect people who want to meet in person to buy and sell Bitcoins for cash, generally without any verification of identity required.
Who decides what a Bitcoin is worth?
The price of Bitcoin fluctuates constantly and is determined by open-market bidding on Bitcoin exchanges, similar to the way that stock and gold prices are determined by bidding on exchanges.
What is Bitcoin mining?
Bitcoin mining refers to the process through which new Bitcoins are created and given to computers helping to maintain the network. The computers involved in Bitcoin mining are in a sort of computational race to process new transactions coming onto the network. The winner — generally the person with the fastest computers — gets a chunk of new Bitcoins, 12.5 of them right now. (The reward is halved every four years.)
There is generally a new winner about every 10 minutes, and there will be until there are 21 million Bitcoins in the world. At that point, no new Bitcoins will be created. This cap is expected to be reached in 2140. So far, about 16 million Bitcoin have been distributed.
Every Bitcoin in existence was created through this method and initially given to a computer helping to maintain the records. Anyone can set his or her computer to mine Bitcoin, but these days only people with specialized hardware manage to win the race.
Are there Bitcoin competitors?
Plenty. But these other virtual currencies do not have as many followers as Bitcoin, so they are not worth as much. As in the real world, a currency is worth only as much as the number of people willing to accept it for goods and services.
Who is Satoshi Nakamoto?
Bitcoin was introduced in 2008 by an unknown creator going by the name of Satoshi Nakamoto, who communicated only by email and social messaging. While several people have been identified as likely candidates to be Satoshi, as the creator is known in the world of Bitcoin, no one has been confirmed as the real Satoshi, and the search has gone on.
Satoshi created the original rules of the Bitcoin network and then released the software to the world in 2009. Satoshi largely disappeared from view two years later. Anyone can download and use the software, and Satoshi now has no more control over the network than anyone else using the software.
API для разработчиков биткоин
Используйте API-интерфейс Blockchain бесплатно, чтобы помочь вам начать создавать приложения для биткойнов.
Обработка платежа
Невероятно простой способ для веб-сайтов получать платежи в биткоинах. Данная услуга абсолютно бесплатна и безопасна. Идеально подходит для бизнеса или личного пользования.
Блок-кошелек
Служба кошелька с блочной связью
Наши API для отправки и получения оплаты от кошельков Blockchain.
Установить через pip:
Добавить следующий репозиторий в ваш pom.xml:
Добавить следующую зависимость в ваш pom.xml:
Установка через NuGet:
Установка через RubyGems:
Скачайте или выполните клонирование репозитория. Скопируйте папку lib/ в ваш проект и добавьте:
Установка через NPM:
Данные транзакций и блоков
API данных Blockchain
Запросить данные JSON по блокам и транзакциям. Почти все данные, которые вы видите на этом веб-сайте, доступны в формате JSON.
Простое API для запросов
Простое API в текстовом формате для запроса данных Blockchain.
Потоковый сокет с низкими временем ожидания, предоставляющий данные о новых блоках и транзакциях. Подпишитесь на уведомления о новых блоках, транзакциях или адресах и получайте JSON-объекты, описывающие транзакции или блоки при возникновении события.
Blockchain.info Время работы
Время работы проверяется каждую минуту и обновляется каждый час.
Bitcoin Mining Hardware Guide
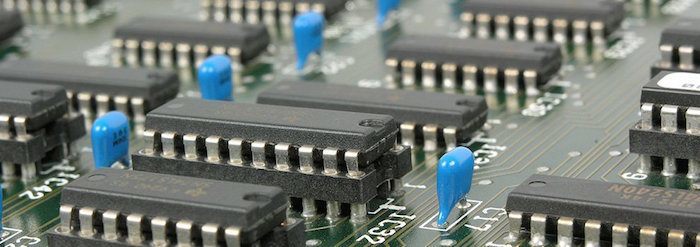
The best Bitcoin mining hardware has evolved dramatically since 2009
At first, miners used their central processing unit (CPU) to mine, but soon this wasn't fast enough and it bogged down the system resources of the host computer. Miners quickly moved on to using the graphical processing unit (GPU) in computer graphics cards because they were able to hash data 50 to 100 times faster and consumed much less power per unit of work.
During the winter of 2011, a new industry sprang up with custom equipment that pushed the performance standards even higher. The first wave of these specialty bitcoin mining devices were easy to use Bitcoin miners were based on field-programmable gate array (FPGA) processors and attached to computers using a convenient USB connection.
FPGA miners used much less power than CPU's or GPU's and made concentrated mining farms possible for the first time.
Today's modern and best bitcoin mining hardware
Application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) miners have taken over completely. These ASIC machines mine at unprecedented speeds while consuming much less power than FPGA or GPU mining rigs. Several reputable companies have established themselves with excellent products.
Bitcoin Mining Hardware Comparison
Currently, based on (1) price per hash and (2) electrical efficiency the best Bitcoin miner options are:
AntMiner S7
AntMiner S9
Best Bitcoin Mining Hardware
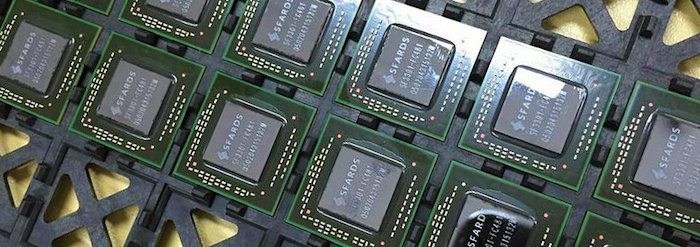
Two major factors go into determining the best bitcoin mining hardware: (1) cost and (2) electricity efficiency.
Bitcoin mining is difficult to do profitably but if you try then this Bitcoin miner is probably a good shot.
ASIC Bitcoin Mining Hardware
Application-specific integrated circuit chips (ASICs) are bitcoin mining hardware created solely to solve Bitcoin blocks. They have only minimal requirements for other normal computer applications. Consequently, ASIC Bitcoin mining systems can solve Bitcoin blocks much quicker and use less less electricity or power than older bitcoin mining hardware like CPUs, GPUs or FPGAs.
As Bitcoin mining increases in popularity and the Bitcoin price rises so does the value of ASIC Bitcoin mining hardware. As more Bitcoin mining hardware is deployed to secure the Bitcoin network the Bitcoin difficulty rises. This makes it impossible to profitably compete without a Bitcoin ASIC system. Furthermore, Bitcoin ASIC technology keeps getting faster, more efficient and more productive so it keeps pushing the limits of what makes the best Bitcoin mining hardware.
Some models of Bitcoin miners include Antminer S5, Antminer U3, ASICMiner BE Tube, ASICMiner BE Prisma, Avalon 2, Avalon 3, BTC Garden AM-V1 616 GH/s, VMC PLATINUM 6 MODULE, and USB miners.
AntMiner U2
BPMC Red Fury USB
GekkoScience
Best Bitcoin Cloud Mining Services
For those not interested in operating the actual hardware then they can purchase Bitcoin cloud mining contracts. Being listed in this section is NOT an endorsement of these services. There have been a tremendous amount of Bitcoin cloud mining scams.
Hashflare Review: Hashflare offers SHA-256 mining contracts and more profitable SHA-256 coins can be mined while automatic payouts are still in BTC. Customers must purchase at least 10 GH/s.
Genesis Mining Review: Genesis Mining is the largest Bitcoin and scrypt cloud mining provider. Genesis Mining offers three Bitcoin cloud mining plans that are reasonably priced. Zcash mining contracts are also available.
Hashing 24 Review: Hashing24 has been involved with Bitcoin mining since 2012. They have facilities in Iceland and Georgia. They use modern ASIC chips from BitFury deliver the maximum performance and efficiency possible.
Minex Review: Minex is an innovative aggregator of blockchain projects presented in an economic simulation game format. Users purchase Cloudpacks which can then be used to build an index from pre-picked sets of cloud mining farms, lotteries, casinos, real-world markets and much more.
Minergate Review: Offers both pool and merged mining and cloud mining services for Bitcoin.
Hashnest Review: Hashnest is operated by Bitmain, the producer of the Antminer line of Bitcoin miners. HashNest currently has over 600 Antminer S7s for rent. You can view the most up-to-date pricing and availability on Hashnest's website. At the time of writing one Antminer S7's hash rate can be rented for $1,200.
Bitcoin Cloud Mining Review: Currently all Bitcoin Cloud Mining contracts are sold out.
NiceHash Review: NiceHash is unique in that it uses an orderbook to match mining contract buyers and sellers. Check its website for up-to-date prices.
Eobot Review: Start cloud mining Bitcoin with as little as $10. Eobot claims customers can break even in 14 months.
MineOnCloud Review: MineOnCloud currently has about 35 TH/s of mining equipment for rent in the cloud. Some miners available for rent include AntMiner S4s and S5s.

Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий