One more step
Please complete the security check to access bitcoinexchangeguide.com
Why do I have to complete a CAPTCHA?
Completing the CAPTCHA proves you are a human and gives you temporary access to the web property.
What can I do to prevent this in the future?
If you are on a personal connection, like at home, you can run an anti-virus scan on your device to make sure it is not infected with malware.
If you are at an office or shared network, you can ask the network administrator to run a scan across the network looking for misconfigured or infected devices.
Cloudflare Ray ID: 422b1a08a3ec8f39 • Your IP : 185.87.51.142 • Performance & security by Cloudflare
How does Bitcoin work?
This is a question that often causes confusion. Here's a quick explanation!
The basics for a new user
As a new user, you can get started with Bitcoin without understanding the technical details. Once you have installed a Bitcoin wallet on your computer or mobile phone, it will generate your first Bitcoin address and you can create more whenever you need one. You can disclose your addresses to your friends so that they can pay you or vice versa. In fact, this is pretty similar to how email works, except that Bitcoin addresses should only be used once.
Balances - block chain
The block chain is a shared public ledger on which the entire Bitcoin network relies. All confirmed transactions are included in the block chain. This way, Bitcoin wallets can calculate their spendable balance and new transactions can be verified to be spending bitcoins that are actually owned by the spender. The integrity and the chronological order of the block chain are enforced with cryptography.
Transactions - private keys
A transaction is a transfer of value between Bitcoin wallets that gets included in the block chain. Bitcoin wallets keep a secret piece of data called a private key or seed, which is used to sign transactions, providing a mathematical proof that they have come from the owner of the wallet. The signature also prevents the transaction from being altered by anybody once it has been issued. All transactions are broadcast between users and usually begin to be confirmed by the network in the following 10 minutes, through a process called mining.
Processing - mining
Mining is a distributed consensus system that is used to confirm waiting transactions by including them in the block chain. It enforces a chronological order in the block chain, protects the neutrality of the network, and allows different computers to agree on the state of the system. To be confirmed, transactions must be packed in a block that fits very strict cryptographic rules that will be verified by the network. These rules prevent previous blocks from being modified because doing so would invalidate all following blocks. Mining also creates the equivalent of a competitive lottery that prevents any individual from easily adding new blocks consecutively in the block chain. This way, no individuals can control what is included in the block chain or replace parts of the block chain to roll back their own spends.
Going down the rabbit hole
This is only a very short and concise summary of the system. If you want to get into the details, you can read the original paper that describes the system's design, read the developer documentation, and explore the Bitcoin wiki.
Bitcoin: What The Heck Is It, And How Does It Work?

The world of finance and economics is pretty complicated as-is, and now there’s “digital money” in the mix making it even worse. Bitcoin is everywhere in the news lately, from hacks to hearings and everything in between. But there are a lot of questions about Bitcoin — starting with, what the heck is all this, anyway? And so, here is everything you wanted to know about Bitcoin, but didn’t actually want to ask your tech-loving, early-adopter friend.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is the world’s biggest cryptocurrency. It was introduced in 2009, and is the longest-standing, best-known, and most widely-traded cryptocurrency.
Generally, Bitcoin with a capital B means the software and the system; bitcoin with a lowercase b means the actual money.
A what?
A cryptocurrency is digital money. It’s a virtual medium of exchange, not issued by, backed by, or tied to any particular nation or government.
It’s the biggest… but there are others?
Yup. The software that runs Bitcoin is open-source, and there are lots of other folks running with it, too. The Guardian covered nine of the biggest in late November. And of course, the internet being what it is, there are novelty versions, like the actually-popular dogecoin or the defunct Coinye West.
If it’s not issued by a government, where does it come from and who keeps track of it?
The acts of generating new bitcoins and of tracking Bitcoin transactions go hand in hand, and both are accomplished through a process known as “mining.” This is where it starts to get a little complicated.
Basically, mining occurs when a computer or a network of computers runs Bitcoin software. That software creates new entries in Bitcoin’s public record of transactions, called block chains. The math is complicated and hard to forge, so the block chain stays accurate. Because anyone can download and install the Bitcoin software for free, the payment processing and record-keeping for Bitcoin is done in a widely distributed way, rather than on one particular server.
When block chains are created, so are new bitcoins — but there’s a hard limit to how many will ever exist. The system was designed to create more bitcoins at first, then to dwindle exponentially over time. The first set of block chains each created 50 bitcoins. The next set each created 25 bitcoins, and so on. New block chains are created roughly every 10 minutes no matter what; when more computers are actively mining, the program they’re running gets harder (and therefore slower) to compensate. The bitcoin FAQ estimates that the final bitcoin will be mined in the year 2140, bringing the permanent circulation to just under 21 million. (Currently, there are roughly 12.4 million bitcoins in the world.)
How much is it worth?
As of this writing, 1 bitcoin = approximately USD $693. However, the bitcoin exchange rate is intentionally highly flexible.
What can you actually buy with bitcoins?
Swanky cocktails in Manhattan, a Tesla car, tickets and concessions for the Sacramento Kings, and anything you want from Overstock.com.
Also, stolen credit card numbers, drugs, guns, and pretty much anything else of questionable legality bought and sold online. It’s great for money laundering too, according to the FBI.
How do you store and spend your bitcoins? Is there any actual physical money?
Even though there are a handful of bitcoin ATMs in the world, bitcoin is not a physical currency. Spending takes place from one user’s virtual wallet to another user’s virtual wallet, via an exchange of public and private security keys.
Physical bitcoins — which can look like coins or bills, or can be any other item — are storage devices for private keys. In one way, storing private keys in physical media is extremely secure; hackers can’t access the box under your bed via a virtual back door. On the other hand, storing private keys in physical media is as insecure as keeping cash on hand; thieves can access the box under your bed via a literal back door. Or you could end up losing the external hard drive with your $5 million on it.
Is this risky? It sounds kind of risky.
There certainly is a lot of volatility in the bitcoin market. The exchange rate has shifted by over $90 this week alone.
The government backing a standard currency — like, say, the US dollar — works hard to keep its money stable. We have the Federal Reserve issuing monetary policy and acting as a central bank to keep the value of a dollar from flying up and down like the stock market does.
For the first three to four years of its life, bitcoin was actually fairly stable, as historical charts show. The price increased very gradually from roughly $0.05 per bitcoin to more like $5 per bitcoin, which is indeed a good rate of return for early investors. And that concept of “investors” is key. Bitcoin is a market full of speculators, and because it’s not tied to anyone’s monetary policy or oversight, it’s prone to boom and bust. Since the beginning of 2013, the value of bitcoin has jumped as high as $1116 and dropped to $539.
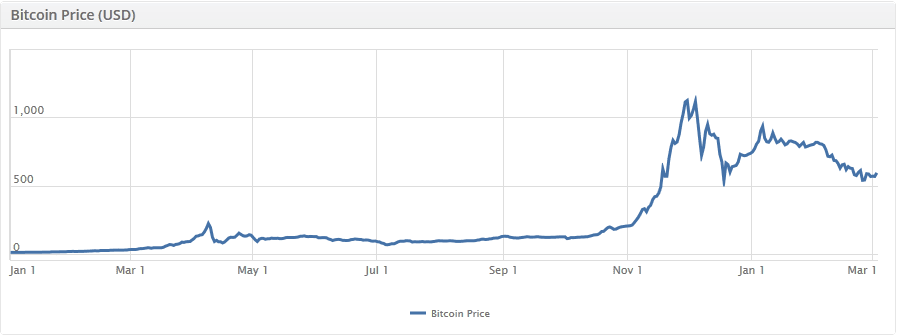
Bitcoin values from Jan. 1 2013 through Mar. 3 2014, via Coinbase.
To the best of my knowledge there’s no intersection at all, in any way, between Bitcoin and banks that the Federal Reserve has the ability to supervise and regulate. So the Fed doesn’t have authority to supervise or regulate Bitcoin in any way.”
Yellen also added, “It’s not so easy to regulate Bitcoin because there’s no central issuer or network operator,” calling Bitcoin a decentralized, global entity.
To Bitcoin developers and users, that global reach and lack of central authority is a core feature, not a bug. Meanwhile, federal prosecutors have sent subpoenas to Mt. Gox, which on Friday declared bankruptcy.
At today’s exchange rate, there’s an equivalent to $8.5 billion out there in the world in bitcoins. It seems likely that regulators and governments will want to keep an eye on where it goes in the future.
Editor's Note: This article originally appeared on Consumerist.
US Search Mobile Web

Welcome to the Yahoo Search forum! We’d love to hear your ideas on how to improve Yahoo Search.
The Yahoo product feedback forum now requires a valid Yahoo ID and password to participate.
You are now required to sign-in using your Yahoo email account in order to provide us with feedback and to submit votes and comments to existing ideas. If you do not have a Yahoo ID or the password to your Yahoo ID, please sign-up for a new account.
If you have a valid Yahoo ID and password, follow these steps if you would like to remove your posts, comments, votes, and/or profile from the Yahoo product feedback forum.
- Vote for an existing idea ( )
- or
- Post a new idea…
- Hot ideas
- Top ideas
- New ideas
- Category
- Status
- My feedback
Improve your services
Your search engine does not find any satisfactory results for searches. It is too weak. Also, the server of bing is often off
I created a yahoo/email account long ago but I lost access to it; can y'all delete all my yahoo/yahoo account except for my newest YaAccount
I want all my lost access yahoo account 'delete'; Requesting supporter for these old account deletion; 'except' my Newest yahoo account this Account don't delete! Because I don't want it interfering my online 'gamble' /games/business/data/ Activity , because the computer/security program might 'scure' my Information and detect theres other account; then secure online activities/ business securing from my suspicion because of my other account existing will make the security program be 'Suspicious' until I'm 'secure'; and if I'm gambling online 'Depositing' then I need those account 'delete' because the insecurity 'Suspicioun' will program the casino game 'Programs' securities' to be 'secure' then it'll be 'unfair' gaming and I'll lose because of the insecurity can be a 'Excuse'. Hope y'all understand my explanation!
I want all my lost access yahoo account 'delete'; Requesting supporter for these old account deletion; 'except' my Newest yahoo account this Account don't delete! Because I don't want it interfering my online 'gamble' /games/business/data/ Activity , because the computer/security program might 'scure' my Information and detect theres other account; then secure online activities/ business securing from my suspicion because of my other account existing will make the security program be 'Suspicious' until I'm 'secure'; and if I'm gambling online 'Depositing' then I need those account 'delete' because the insecurity 'Suspicioun' will program the casino game 'Programs' securities' to be… more
chithidio@Yahoo.com
i dont know what happened but i can not search anything.
Golf handicap tracker, why can't I get to it?
Why do I get redirected on pc and mobile device?
Rahyaftco@yahoo.com
RYAN RAHSAD BELL literally means
Question on a link
In the search for Anaïs Nin, one of the first few links shows a picture of a man. Why? Since Nin is a woman, I can’t figure out why. Can you show some reason for this? Who is he? If you click on the picture a group of pictures of Nin and no mention of that man. Is it an error?
Repair the Yahoo Search App.
Yahoo Search App from the Google Play Store on my Samsung Galaxy S8+ phone stopped working on May 18, 2018.
I went to the Yahoo Troubleshooting page but the article that said to do a certain 8 steps to fix the problem with Yahoo Services not working and how to fix the problem. Of course they didn't work.
I contacted Samsung thru their Samsung Tutor app on my phone. I gave their Technican access to my phone to see if there was a problem with my phone that stopped the Yahoo Search App from working. He went to Yahoo and I signed in so he could try to fix the Yahoo Search App not working. He also used another phone, installed the app from the Google Play Store to see if the app would do any kind of search thru the app. The Yahoo Search App just wasn't working.
I also had At&t try to help me because I have UVERSE for my internet service. My internet was working perfectly. Their Technical Support team member checked the Yahoo Search App and it wouldn't work for him either.
We can go to www.yahoo.com and search for any topic or website. It's just the Yahoo Search App that won't allow anyone to do web searches at all.
I let Google know that the Yahoo Search App installed from their Google Play Store had completely stopped working on May 18, 2018.
I told them that Yahoo has made sure that their Yahoo members can't contact them about anything.
I noticed that right after I accepted the agreement that said Oath had joined with Verizon I started having the problem with the Yahoo Search App.
No matter what I search for or website thru the Yahoo Search App it says the following after I searched for
www.att.com.
WEBPAGE NOT AVAILABLE
This webpage at gttp://r.search.yahoo.com/_ylt=A0geJGq8BbkrgALEMMITE5jylu=X3oDMTEzcTjdWsyBGNvbG8DYmyxBHBvcwMxBHZ0aWQDTkFQUEMwxzEEc2VjA3NylRo=10/Ru=https%3a%2f%2fwww.att.att.com%2f/Rk=2/Es=plkGNRAB61_XKqFjTEN7J8cXA-
could not be loaded because:
net::ERR_CLEARTEXT_NOT_PERMITTED
I tried to search for things like www.homedepot.com. The same thing happened. It would say WEBPAGE NOT AVAILABLE. The only thing that changed were all the upper and lower case letters, numbers and symbols.
Then it would again say
could not be loaded because:
net::ERR_CLEARTEXT_NOT_PERMITTED
This is the same thing that happened when Samsung and At&t tried to do any kind of searches thru the Yahoo Search App.
Yahoo needs to fix the problem with their app.
Yahoo Search App from the Google Play Store on my Samsung Galaxy S8+ phone stopped working on May 18, 2018.
I went to the Yahoo Troubleshooting page but the article that said to do a certain 8 steps to fix the problem with Yahoo Services not working and how to fix the problem. Of course they didn't work.
I contacted Samsung thru their Samsung Tutor app on my phone. I gave their Technican access to my phone to see if there was a problem with my phone that stopped the Yahoo Search App from working. He went to Yahoo and… more
How does bitcoin work
I read below message on Internet, just sharing:
*BITCOIN* How it works?
A lot of monkeys lived near a village
One day a merchggant came to the village to buy these monkeys!
He announced that he will buy the monkeys @ $100 each.
The villagers thought that this man is mad
They thought how can somebody buy stray monkeys at $100 each?
Still, some people caught some monkeys and gave it to this merchant and he gave $100 for each monkey.
This news spread like wildfire and people caught monkeys and sold it to the merchant
After a few days, the merchant announced that he will buy monkeys @ 200 each
The lazy villagers also ran around to catch the remaining monkeys!
They sold the remaining monkeys @ 200 each.
Then the merchant announced that he will buy monkeys @ 500 each!
The villagers start to lose sleep! . They caught six or seven monkeys, which was all that was left and got 500 each.
The villagers were waiting anxiously for the next announcement
Then the merchant announced that he is going home for a week. And when he returns, he will buy monkeys @ 1000 each!
He asked his employee to take care of the monkeys he bought. He was alone taking care of all the monkeys in a cage.
The merchant went home.
The villagers were very sad as there were no more monkeys left for them to sell it at $1000 each
Then the employee told them that he will sell some monkeys @ 700 each secretly.
This news spread like fire. Since the merchant buys monkey @ 1000 each, there is a 300 profit for each monkey.
The next day, villagers made a queue near the monkey cage.
The employee sold all the monkeys at 700 each. The rich bought monkeys in big lots. The poor borrowed money from money lenders and also bought monkeys!
The villagers took care of their monkeys & waited for the merchant to return.
But nobody came! . Then they ran to the employee.
But he has already left too !
The villagers then realised that they have bought the useless stray monkeys @ 700 each and unable to sell them!
The Bitcoin will be the next monkey business
It will make a lot of people bankrupt and a few people filthy rich in this monkey business.
That' how it will work

What Is Bitcoin:
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency, or a digital currency, that uses rules of cryptography for regulation and generation of units of currency. Bitcoin falls under the scope of cryptocurrency and was the first and most valuable among them. It is commonly called a decentralised digital currency.
A cryptocurrency (or crypto currency) is a digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange that uses cryptography to secure its transactions, to control the creation of additional units, and to verify the transfer of assets. Cryptocurrencies are classified as a subset of digital currencies and are also classified as a subset of alternative currencies and virtual currencies.
How does Bitcoin works:
Bitcoins are completely virtual coins designed to be ‘self-contained’ for their value, with no need for banks to move and store the money.
Once you own bitcoins, they possess value and trade just as if they were nuggets of gold in your pocket. You can use your bitcoins to purchase goods and services online, or you can tuck them away and hope that their value increases over the years. Bitcoins are traded from one personal 'wallet' to another.
A wallet is a small personal database that you store on your computer drive, on your smartphone, on your tablet, or somewhere in the cloud.
Bitcoin shares some similarities with real-world currencies, particularly its growing acceptance as a form of payment with more and more merchants, retailers and individuals, both online and offline. You can buy Microsoft products with Bitcoin, buy airline tickets through Expedia, or buy gift cards to superstores like Walmart.
Yet Bitcoin is also very different from traditional currencies. Unlike dollars or pounds, Bitcoin isn't backed by any government. It's a completely decentralized form of money. Bitcoin isn't linked to any sort of central banking system or issuing authority, and that's a big part of its appeal — instead of being swallowed into a system that's often sullied by human greed and manipulation, this currency exists in an online world driven by mathematics and clever encryption protocols.
You can use Bitcoin for all sorts of real transactions. To do so, you first buy bitcoins however you like, either through your credit card, a bank account or even anonymously with cash. Then your bitcoins are transferred directly into your Bitcoin wallet, and you can send and receive payments directly to a buyer or seller without the need for a typical go-between, such as a bank or credit card company.
Here Iam sharing one video to know more information about how bitcoin is working
Who is Behind Bitcoin:
Satoshi Nakamoto is the name used by the unknown person or people who designed bitcoin and created its original reference implementation. As part of the implementation, they also devised the first block chain database. In the process they were the first to solve the double-spending problem for digital currency. They were active in the development of bitcoin up until December 2010.
Is Bitcoin Legal:
The legal status of bitcoin varies substantially from country to country and is still undefined or changing in many of them. Whilst the majority of countries do not make the usage of bitcoin itself illegal, its status as money (or a commodity) varies, with differing regulatory implications. While some countries have explicitly allowed its use and trade, others have banned or restricted it. Likewise, various government agencies, departments, and courts have classified bitcoins differently.
But for the most part it remains relatively safe to use as long as it is not tied to illicit purchases or activities. Many countries have issued statements indicating that bitcoin and other digital currencies are not regulated and do not exist as officially sanctioned currencies: a status that could put users at risk but would not have them violating any laws. Bitcoin is outright illegal in some countries, such as Iceland.
Depending on where and how you utilize bitcoin, it is important to remain up-to-date on the latest regulations concerning the digital currency. As laws change across borders, governing bodies and, increasingly, as the platform gains popularity, questions about bitcoin’s legality will continue to be raised.


It is the first Decentralized currency
I know what you are thinking. And that is : “If I hear the words “Decentralized currency” one more time, I am gonna personally find Satoshi Nakamoto and decentralize him”.
Right, so let’s see what Decentralized currency means later. For now, let’s see what is Currency.
Currency is a tool which we use to exchange values. Earlier people were using Gold and other valuable metals to exchange with goods required by them. Gold was tangible. If a certain amount of Gold were to be in your hand, it basically meant you owned it.
Due to Gold’s obvious disadvantages, we started using paper money. What we currently are acquainted with is something called Fiat Currency. Which means we are basically assuming that a particular piece of paper is worth some value.
*I promise to pay the bearer(of this note) the sum of one hundred rupees*
Nowadays most of the money is just in the form of numbers. So there is a possibility that the same money can be used for multiple transactions. This problem is called as “Double Spending”.
To avoid this, banks keep a ledger to keep track of all the transactions essentially acting as a Centre. Hence our conventional money is called as Centralized Currency.
Some computer scientists were not satisfied with a third party(bank) keeping track of transactions. This is when Satoshi Nakamoto comes in and proposes and entirely different solution where there is no 3rd party involved(decentralized currency). BITCOIN
Decentralized currency is like Internet. There is no one entity owning it(yet).
The deal with Bitcoin is that all the transactions are public and the ledger recording those transactions are public. This ledger is called as a BLOCKCHAIN. Everyone can have a copy of it and tally their transactions.
There might be issues regarding security but think of hacking a bitcoin blockchain as hacking english dictionary. You can change the meaning of a word in one dictionary. But not in every other copy in the world.
If you are still reading, I will add more content on it in future.

Bitcoins need block-chain but the vice-versa is not true: Block-chain exists as a technology even without Bitcoins.
For instance, assume that I own a Bitcoin and I want to transfer it to you for any reason in the world: as a payment, as a present, charity or whatever you can think.
To make it simple, let’s consider that a Bitcoin is nothing more than a text file and by copying the file to your USB and uploading it to your Dropbox, I can let you have my Bitcoin file.
Suppose I add the file to your Dropbox. At this point, there are two copies of "my" Bitcoin: the one on my hard-drive and the one in your Dropbox.
Let's draw a parallel analogy for a moment. If we try and make a copy of a 100 Rupee note, no one would take the copy of the note as a payment, would they? We would be so poor at making the 100 Rupee note copy that anyone would spot it is a fake. Instead, a copy of a Bitcoin file, is a perfect bit by bit copy. Do you agree?
We all agree to the point that the 100 rupee cannot be replicated easily. If Bitcoin is a currency like the Rupee, why is it "acceptable" to copy-paste a Bitcoin file instead, and not go to jail?"
More to the point, how do we make sure the same Bitcoin is not used multiple times to pay for different goods in different transactions (you might have heard before of the double spending issue)?
Beacuse spending of a Bitcoin and a Rupee happens through entirely different mechanisms and conventions.
Whilst 100 Rupee can physically slip from my wallet to your wallet, to achieve the same "transfer" for a Bitcoin, we need to use the related Bitcoin network.
To our previous example, the same Bitcoin is on my hard-drive and in your Dropbox. If we both can use it to pay for goods, then the Bitcoin infrastructure cannot work as a currency, can it? It would allow double spending of the same Bitcoin. Hence a Bitcoin will never be able to hold a real value, because it can be easily duplicated. Instead a Bitcoin is more like gold. It cannot be duplicated.
What gives to Bitcoin which, as we said earlier, is nothing more than a text file, the property of being like gold instead? Let's leave a little suspense here.
To transfer a Bitcoin from my wallet to your wallet, we need to use the Bitcoin network. And what the Bitcoin network does, among other things,it ensures that only the first one of us who use the Bitcoin in an actual payment will be able to actually spend it.
How does the network makes sure that Bitcoin file is spent only once? The Bitcoin block-chain network will have a registered transaction where that Bitcoin (the code contained in the Bitcoin text file) has been used for payment. If someone tries to use the same file again, the network will find it out and reject the transaction.
So, the block-chain mechanism gives Bitcoin characteristics that resemble those of gold. That's why, the block-chain network itself creates Bitcoins by "mining" them.
Guide: What is Bitcoin and how does Bitcoin work?
The value of virtual currency Bitcoin is at the highest it's ever been - one Bitcoin is now worth more than £7,000 - and its value could go even higher.
But what is Bitcoin and how does it all work?
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin, often described as a cryptocurrency, a virtual currency or a digital currency - is a type of money that is completely virtual.
It's like an online version of cash. You can use it to buy products and services, but not many shops accept Bitcoin yet and some countries have banned it altogether.
The physical Bitcoins you see in photos are a novelty. They would be worthless without the private codes printed inside them.
How does Bitcoin work?
Each Bitcoin is basically a computer file which is stored in a 'digital wallet' app on a smartphone or computer.
People can send Bitcoins (or part of one) to your digital wallet, and you can send Bitcoins to other people.
Every single transaction is recorded in a public list called the blockchain.
This makes it possible to trace the history of Bitcoins to stop people from spending coins they do not own, making copies or undo-ing transactions.
How do people get Bitcoins?
There are three main ways people get Bitcoins.
- You can buy Bitcoins using 'real' money.
- You can sell things and let people pay you with Bitcoins.
- Or they can be created using a computer.
How are new Bitcoins created?
In order for the Bitcoin system to work, people can make their computer process transactions for everybody.
The computers are made to work out incredibly difficult sums. Occasionally they are rewarded with a Bitcoin for the owner to keep.
People set up powerful computers just to try and get Bitcoins. This is called mining.
But the sums are becoming more and more difficult to stop too many Bitcoins being generated.
If you started mining now it could be years before you got a single Bitcoin.
You could end up spending more money on electricity for your computer than the Bitcoin would be worth.
Why are Bitcoins valuable?
There are lots of things other than money which we consider valuable like gold and diamonds. The Aztecs used cocoa beans as money!
Bitcoins are valuable because people are willing to exchange them for real goods and services, and even cash.
Why do people want Bitcoins?
Some people like the fact that Bitcoin is not controlled by the government or banks.
People can also spend their Bitcoins fairly anonymously. Although all transactions are recorded, nobody would know which 'account number' was yours unless you told them.
Is it secure?
Every transaction is recorded publicly so it's very difficult to copy Bitcoins, make fake ones or spend ones you don't own.
It is possible to lose your Bitcoin wallet or delete your Bitcoins and lose them forever. There have also been thefts from websites that let you store your Bitcoins remotely.
The value of Bitcoins has gone up and down over the years since it was created in 2009 and some people don't think it's safe to turn your 'real' money into Bitcoins.
How does bitcoin work
Still have a question? Ask your own!

Here’s an “explain it like I’m 5” from Reddit:
Imagine you have a hat with 100 pieces of paper in it, numbered 1 to 100. You pull out a piece of paper every minute and look at what you got (then put it back and shake up the hat). If it is lower than 20, you win, and you would win on average every five minutes. If you started checking numbers faster than every minute, I could slow down how often you win by making the highest winning number 15 instead of 20.
Bitcoin mining is kind of like that, but instead of 1 to 100 numbers, there are 1 to 1.1579E+77 possible numbers that you get when you take the hash of some data, and Bitcoin awards you 50 BTC if you find a hash of the current transaction block that is 1.7248E+61 or smaller.
A SHA hash is a complex mathematical formula that original data is put through, and the formula creates a number on the other side, like a 'signature' of the original data. Other hashes you might be familiar with in computers are MD5 or CRC. Since hashing the same transaction block over and over would always give you the same SHA hash, your computer adds some more random data to the end of a transaction block (called a nonce), to change the hash that comes out. SHA is cryptographically secure, in that it is impossible to tell what the hash will be from the nonce you add, so there is no shortcut around just trying billions of different nonces and checking the hash that is generated.

Mining is simply the process of solving a very complicated math problem via brute force until someone in the network gets the “right” answer. The problem they are solving is similar in structure to “find two prime numbers that multiple to the value y”, where the only way to solve the problem is to randomly try inputs until you get the right answer.
When a node is successful, they get the right to put the next block on the blockchain and get a reward for this work (currently
12 BTC). The rest of the network then verifies this answer and, when accepted, moves on to solving the next problem.
Without getting into the details of what problem theses nodes are solving and how the network handles transactions, this is the basics of what mining entails.

This is my understanding, from end to end.
All nodes keep a local copy of the grand ledger that is the blockchain on their computer. As nodes create transactions, they are broadcasted to their neighbors, which their neighbors broadcast to their neighbors, thus propagating it through the network. Certain nodes, fulfilling the special role of miner, receive and collect these transactions into blocks. In an attempt to keep this explanation simple, I will skip the details on how a group of transactions gets collected into a block. Just know there are certain rules followed to do so.
Now that this miner has the block she would like to attempt to "mine" next, she starts the "mining" process, which is to run the Proof-of-Work algorithm*. This process does several things, most prominently providing verification of the transactions and confirming them so they can be added to the blockchain (read ledger). She attempts to solve a hash puzzle. She takes certain data related to the block, combine it with a nonce (number used once), and runs it through a hash function (SHA-256). She is attempting to get an output that has a certain number of leading zeroes (i.e. 000000. 11101). This target number is set by a difficulty that is updated every 2016 blocks such that it takes about 10 minutes for the network as a whole to find a new block.
Once the miner meets the target output, she did it! Time to rejoice and collect the reward, currently at 25 BTC. This reward halves every 210,000 blocks, so the reward should go down to 12.5 sometime in 2017. In addition to this nominal reward, miners get all transaction fees that may have been included in the block.
There is the idea of "longest chain" in Bitcoin, where the longest chain is considered the true chain, as long as all the math holding it together checks out. It is written deep in the client software of Bitcoin for nodes to follow the longest chain. Our miner appends her newly minted block at the end of her local chain, making hers the longest. The surrounding nodes notice this and quickly check her math, and if everything checks out, update their own local copies of the blockchain to match this new, longest chain. This repeats and the new chain propagates through the network.
Bitcoin and its underlying technology is a very complex subject, and at some point trying to reduce it to a simple digest is impossible. Hopefully this helps; keep doing research and asking questions and I promise, one day it will all click together. Good Luck!
*A note on POW. Mining rigs today can complete millions of these "hash puzzle" calculations every second. Take all the miners, doing million of calculations per second, for 10 minutes. It certainly isn't computationally trivial to mine a block!! This is where much of the security in this method of mining comes from (there are other form of mining algorithms, but we'll save that for another time).
How does a bitcoin wallet work?
As we’ve seen already, there are many different kinds of bitcoin wallets (also called bitcoin clients). Each has different characteristics and functionalities, but each works in basically the same way: they store your public and private keys.
Your bitcoins – or rather, the pieces of code that represent them – are not actually stored in your wallet. They are stored on the blockchain, which in turn is stored on node computers all around the world.
What your wallet contains is your bitcoin address, which is the same as your randomly generated public key (a long string of numbers and characters). Anyone can see this, it’s public information. The wallet also contains the private key that goes with that address/public key. Without the combination of the two keys, you can’t use your bitcoins. Actually, most wallets contain several addresses, and hold the public and private key pairings that make each of them work.
Obviously, most bitcoin wallets today do a lot more than that. They also relate your public and private keys to the bitcoins that match those keys, and display the list of related transactions and the current balance in a clean user interface (ie. a nice, easy-to-understand format).
But it’s important to understand that the wallet doesn’t actually contain your bitcoin. It contains permission to spend your bitcoin. And if you lose access to that permission to spend, then you effectively also lose your bitcoins, because you no longer have access to them. That is why it is so important to keep the keys secure.
Some wallets, especially the older ones, are full node wallets. This means that you download the entire blockchain, and act as a relayer or transmitter of transactions, even those that you had nothing to do with. You receive transactions from nodes and pass them on to other nodes, and thus contribute to the updating of the bitcoin network. While no actual work on your part is involved (the transmitting is done automatically), it is onerous – the blockchain occupies approximately 40GB of memory.
Most wallets, however, are “thin wallets”, or an SPV wallet (which stands for Simplified Payment Verification). If you have a wallet on your mobile phone, it’s almost certainly one of these, and an increasing number of desktop wallets are also offering this option. SPV wallets do not download the entire blockchain, they only download block headers. There are concerns that this weakens the security of the network as a whole, since they cannot tell the difference between a block with valid transactions and one with invalid ones. (Segregated Witness offers a potential solution to this problem, but the project is still at the testing phase.) But they rely on nodes to check the transactions for validity, and assume that after a certain number of blocks have been added on top, a transaction can be counted on to be correct.
Wallet technology is evolving rapidly in terms of efficiency and functionality, so this overview does not hope to cover all wallet types, but the basic principle is the same for most: wallets hold your keys, not your bitcoins, although the distinction is actually not that relevant for the average user. Bitcoin wallets are a fundamental piece in the path to increase bitcoin use beyond geeks and techies, as it is the only face of bitcoin that most will ever see. Wallet ease of use and security will increase confidence in transactions, while at the same time encourage more use cases. With more users comes even more innovation, and the entire sector – from front-end wallets to back-end miners and including the many applications in between – benefits.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
Bitcoin is maintained by a peer-to-peer network, which allows Bitcoin transactions (the transfer of Bitcoin value from one Bitcoin address to another using cryptographic algorithms) to occur directly between a buyer and seller. This direct connection of buyer and seller eliminates the need for a financial intermediary such as a central bank or Federal Reserve. Instead of using an intermediary, Bitcoin transactions are facilitated by an independent collective network of Bitcoin “miners” that process transactions and validate Bitcoin authenticity and proof of ownership. Anyone with an internet connection can mine Bitcoins by running Bitcoin mining software.
The sum total of the miners’ collective computing power is called the “Bitcoin Network.” The larger the Bitcoin Network, the more secure it becomes. The reason for this is because it becomes more computationally impractical for malicious software to attack the Bitcoin Network as the Network expands its computer resources. The only way a malicious attack could effectively be made on the Bitcoin Network is if the attack came from a network larger and with more processing power than the Bitcoin Network. Whereas banks charge transaction fees to recoup the billions of dollars invested in infrastructure to facilitate transactions, Bitcoin miners have the opportunity to receive a transaction fee for their expenditure computing power and electricity.
Transaction fees between independent Bitcoin buyers and sellers are voluntary and are set by the parties; transactions with the highest fees will almost always be processed faster, but even transactions with no fees will eventually be processed. The transaction fee is designed to incentivize people to become miners (or join a mining pool) in order to expand the Bitcoin network’s available computer resources that are required to verify transactions. Transaction fees for converting Bitcoin into other currencies and merchant transactions operate differently and are established by the Bitcoin service provider such as CoinBase.com and BitPay.com. Currently, the standard transaction fee is competitively bench-marked at 1%.
The Bitcoin network of miners performs two vital functions: it processes and validates Bitcoin transactions using sophisticated algorithms, and it introduces new Bitcoin into the Bitcoin economy by a process known as “mining.”
How does bitcoin work
Like email, bitcoin is a protocol. Where email is a protocol for sending messages over the internet, bitcoin is a protocol for sending money over the internet. The bitcoin protocol defines the rules of a payment network, called bitcoin, that uses a currency, also called bitcoin, to pay computers around the world for securing the network. The software that implements the bitcoin protocol uses a special branch of mathematics called cryptography to ensure the security of every bitcoin transaction.
The rules of the bitcoin protocol include the requirement that a user cannot send the same bitcoin more than once and a user cannot send bitcoin from an address for which they do not possess the private key. If a user tries to create a transaction that breaks the rules of the bitcoin protocol, it will automatically be rejected by the rest of the bitcoin network.
Note: this is a simplified explanation of how bitcoin works. You can learn more about the technical details of how bitcoin works in the bitcoin whitepaper and the bitcoin wiki .
Bitcoin addresses
Bitcoin ownership is secured by a special code called a cryptographic key pair. Each key pair is made of two keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is transformed into a “bitcoin address” that is used to receive bitcoin transactions. The private key is used to make a digital signature that sends bitcoin from one address to another.
A bitcoin address looks like this:
19wrFHPLc23rqeeZx1YAb5wjNLr8oDMg7G
Bitcoin addresses are often turned into QR codes so they can easily be scanned by a smartphone camera:

(Note: bitcoin sent to that address cannot be spent, so don’t try it unless you like throwing away money!)
Like an email address, a bitcoin address can be shared with anyone that the owner wants to receive a bitcoin payment from. Private keys, on the other hand, should not be shared. Anyone who possesses the private key to a bitcoin address can spend the bitcoin sent to that address.
Bitcoin wallets
Bitcoin wallets are software applications that implement the rules of the bitcoin protocol to ensure that users can easily and securely send and receive bitcoin transactions. Bitcoin wallets also show information about each transaction that is relevant to the wallet, including transactions sent and received by the wallet.
To receive payments, a wallet will usually generate a new address for each transaction. To send payments, the wallet will digitally sign transactions with the correct private keys and broadcast transactions to the bitcoin network. Once a transaction is confirmed by the network, the wallet will no longer be able to spend the same bitcoins used in the transaction again.

The bitcoin network
The bitcoin network is made up of thousands of computers around the world called “bitcoin nodes” and “bitcoin miners”. Bitcoin is an open network, meaning anyone can run bitcoin software to become a bitcoin node or a bitcoin miner.
Bitcoin nodes set and enforce the rules of the bitcoin protocol, and bitcoin miners process transactions and add them into “blocks” that are confirmed by bitcoin nodes. The bitcoin protocol is designed to ensure that new blocks are created and confirmed approximately every ten minutes.
To secure each block of bitcoin transactions, bitcoin miners must use their computing power to solve a unique math problem provided by the bitcoin software. If a bitcoin miner can solve the math problem before any other bitcoin miner, they will win a “block reward” that consists of all the fees paid by each transaction included in their block, as well as newly generated bitcoin.
Bitcoin miners have a strong incentive to produce blocks that follow the rules of the bitcoin protocol. If a bitcoin miner produces a block that does not follow the rules of the bitcoin protocol, then bitcoin nodes will reject the block and the miner will lose out on their chance to win the block reward.
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий